Ciencia Y Tecnología
Standing waves of fire!
Check out Audible: http://bit.ly/AudibleVe
Fysikshow: http://bit.ly/Fysikshow - I'm hosting Michio Kaku in Melbourne ONLY: http://bit.ly/VeKakuTickets
Rubens' Tube is an awesome demo and here we take it to the next level with a two-dimensional 'Pyro Board'. This shows unique standing wave patters of sound in the box.
The pressure variations due to the sound waves affect the flow rate of flammable gas from the holes in the Pyro Board and therefore affect the height and colour of flames. This is interesting for visualizing standing wave patterns and simply awesome to watch when put to music. Thank you to Sune Nielsen and everyone at Aarhus for sharing this demonstration with me! And thanks for having me at your conference.
Music by Kevin MacLeod, www.Incompetech.com "Ice Flow"
What happens when a super long slinky is dropped?
I actually have many, many more questions and answers so if you want to see them, like this video and let me know in the comments and I will edit them. Thank you for your support! I wouldn't have gotten this far without you.
This fungus lives on your scalp and may affect the genes you express.
Check out Head & Shoulders research on getting rid of dandruff: https://ve42.co/HS
Animation by Pindex: https://ve42.co/pindex
When I started this project, I wasn't sure what caused dandruff and I also didn't think much science would go into making a shampoo like Head & Shoulders. So what I learned really surprised me:
There are hundreds of scientists working on this shampoo. They run crazy-sounding experiments like hanging hair near Tokyo highways to understand how real-world environments deposit dirt on hair. They use sophisticated scientific techniques like electron microscopes, nuclear magnetic resonance and gene sequencing to study dandruff on the molecular level.
In fact they sequenced the entire genome of Malassezia globosa in 2002, one year after the human genome project. Their findings are published in international refereed journals. What they have found is that the Malassezia fungi create free fatty acids as byproducts of their digestion, which for some people create irritation and lead to hyper-proliferation of skin cells, flaking, histamines, inflammatory cytokines, and blood proteins reaching the surface of the skin. These findings indicate the unhealthiness of dandruff scalp and suggest a possible remedy - controlling the metabolism of the Malassezia fungi. This is achieved using different active ingredients in different products and different parts of the world, including zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, and piroctone olamine. With the reduction of irritants, the scalp actually expresses different genes, producing a signature more similar to a non-dandruff baseline scalp.
Music from Epidemic Sound: http://epidemicsound.com
Music also by Kevin MacLeod: http://incompetech.com
Thank you to Rodney Fox for sharing his story. He was attacked by a shark 50 years ago - Dec. 8 1963. If you're interested in his book or in going shark cage diving in South Australia, check out: http://bit.ly/rodneyfox
Vitamins are 13 molecules essential for life that our bodies can't make themselves.
Watch Vitamania here: https://ve42.co/vita
Now available worldwide, except France and Germany where it will be broadcast on ARTE soon. Subscribe on the Vitamania website for updates.
Use #vitamania to join the conversation on Twitter and Facebook.
Vitamania is a Genepool Productions feature documentary for SBS Australia, CuriosityStream, and ARTE France. Principal production investment from Screen Australia, in association with Film Victoria.
Droplets levitate on a bath of liquid nitrogen and are spontaneously self-propelled. Thanks Audible! Start a 30-day trial and your first audiobook is free. Go to https://audible.com/VERITASIUM or text VERITASIUM to 500500.
Special thanks to Dr. Anaïs Gauthier
Physics of Fluids: https://pof.tnw.utwente.nl/
Self-propulsion of inverse Leidenfrost drops on a cryogenic bath
Anaïs Gauthier, Christian Diddens, Rémi Proville, Detlef Lohse, and Devaraj van der Meer
PNAS January 22, 2019 116 (4) 1174-1179; published ahead of print January 22, 2019
https://www.pnas.org/content/116/4/1174
For a detailed description of the setup:
http://www.lps.ens.fr/~adda/pa....piers/Langmuir2016.p
And self-propulsion is also seen: http://www.lps.ens.fr/~adda/pa....piers/InvLeidenfrost
Other recent (hot) Leidenfrost experiments that might be interesting:
* Leidenfrost wheels: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glRGl-eYuXo
* Leidenfrost maze: https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=174&v=vPZ7sx3EwUY
* Leidenfrost explosions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z0sp3AjgUy4
Special thanks to Patreon supporters:
Donal Botkin, James M Nicholson, Michael Krugman, Nathan Hansen, Ron Neal, Stan Presolski, Terrance Shepherd
Thanks to Prof. Kevin McKeegan at UCLA for the liquid nitrogen
Filming by Raquel Nuno
Additional animations by Alan Chamberlain
Apollo astronauts trained in nuclear bomb craters at the Nevada National Security Site. But why?Thanks Audible! Start listening with a 30-day trial and your first audiobook plus two Audible Originals free when you go to http://audible.com/veritasium or text veritasium to 500500
I found this story fascinating because in a way a nuclear bomb crater is more like a meteorite impact site than an impact site itself. Consider: Barringer Crater was claimed to be a meteorite impact site but geologists dismissed it as a volcanic formation. It was only after studying nuclear bomb craters and the minerals found there that geologists concluded the energy and pressures that created Barringer Crater were too high to be from volcanic activity and therefore must have formed from a meteorite impact.
Special Thanks to:
Nevada National Security Site
The National Atomic Testing Museum
Jonny Hyman and Verse: https://youtu.be/7bUUGzi-AAY
Active Galactic for footage of craters in Arizona: https://youtu.be/yhoooBpndog
Special thanks to Patreon supporters:
a human, Alfred Wallace, Arjun Chakroborty, Brent Stewart, Bryan Baker, Chris Vargas, Chuck Lauer Vose, Clip Tree, Coale Shifflett, Colin Bellmore, DALE HORNE, Daniel Milum, Donal Botkin, Eric Velazquez, Illya Nayshevsky, James Knight, James Wong, Jasper Xin, Joar Wandborg, Johnny, June Kang, Kevin Beavers, kkm, Leah Howard, Listen Money Matters, Lyvann Ferrusca, Manuel Zürcher, Mathias Göransson, Michael Bradley Wirz, Michael Krugman, Mohammed Al Sahaf, OddJosh, Philipp Volgger, Pindex, Roberto Rezende, Robin DeBank, Ron Neal, Sam Lutfi, Stan Presolski, Tige Thorman, Warrior8252
Filmed by Raquel Nuno
Story and Editing by Derek Muller and Jonny Hyman
Music and Animation by Jonny Hyman
Produced by Casey Rentz
Have your voice heard at the UN Climate Summit in NYC, September 23: http://bit.ly/WhyNotVe
Interview filming by Chris Cassella: http://bit.ly/ScienceAlertVe
Sound waves in a tube of gas create flames of different heights that dance to the music. A metal tube with holes in it is filled with gas. The gas is lit to create a row of tiny flames. A speaker at one end plays sound into the tube, which creates a standing wave of sound: areas where air molecules are vibrating rapidly separated by areas where the air is fairly still. This produces the different heights of flames and allows the wavelength of the sound wave to be estimated.
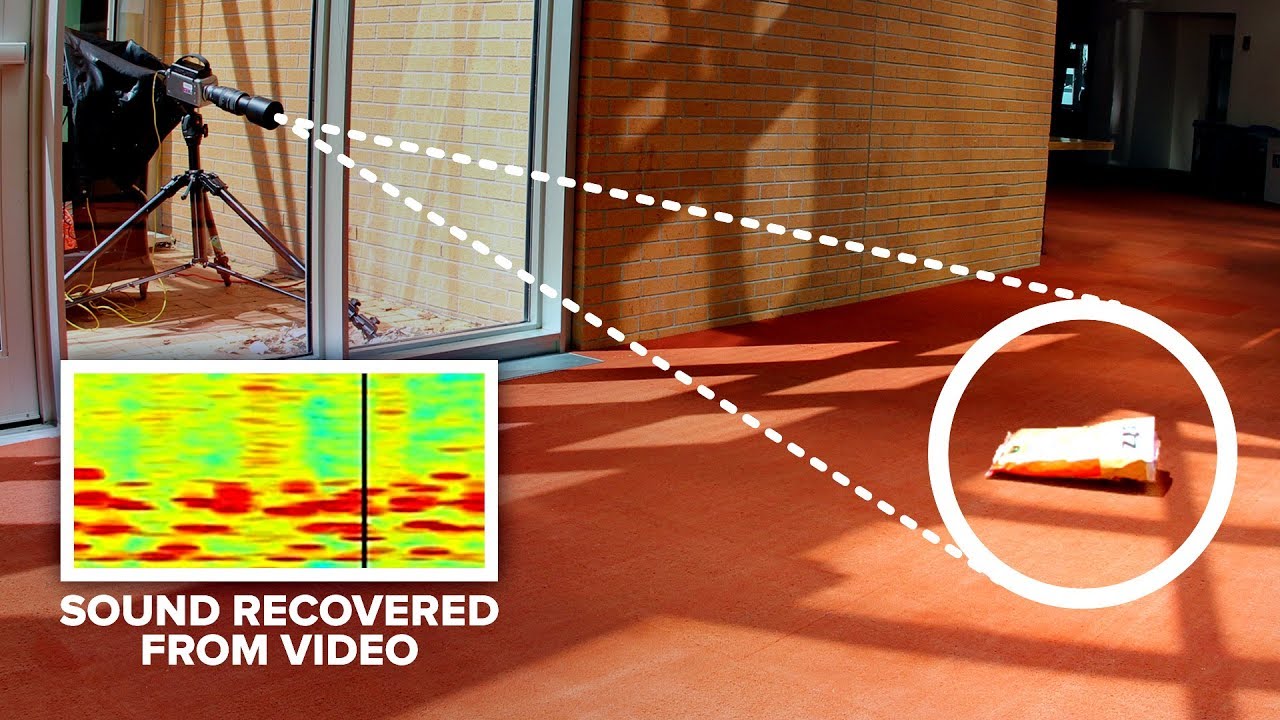
Is it possible to reconstruct sound from high-speed video images?
Part of this video was sponsored by LastPass: http://bit.ly/2SmRQkk
Special thanks to Dr. Abe Davis for revisiting his research with me: http://abedavis.com
This video was based on research by Dr. Abe Davis and colleagues. I found out about this work years ago and was fascinated by the way he was able to capture vibration information in image-only video. I always imagined the motions of objects would be visible as when recording a tuning fork in slow motion - so deriving sound from high speed images seemed a feasible task. But the reality is much more difficult.
Sound vibrations only cause objects to wiggle by about a micrometer. This is much smaller than a pixel, so the algorithm must understand the characteristics of the image. A move in one direction should cause some pixels to lighten slightly, while others darken - and this behavior is correlated along the edges of the image. So noise can be reduced because it's random over the image and there are enough places to sample that you can get it to cancel out.
Something I'm wondering now is - would it be possible to capture sound in a single image? I'm thinking it would have to be an image of a large object or space because the wavelengths of typical sounds are quite long. Maybe a high frequency sound could be imaged in a suitable medium...
Animations by Alan Chamberlain
Music from http://epidemicsound.com "Seaweed"
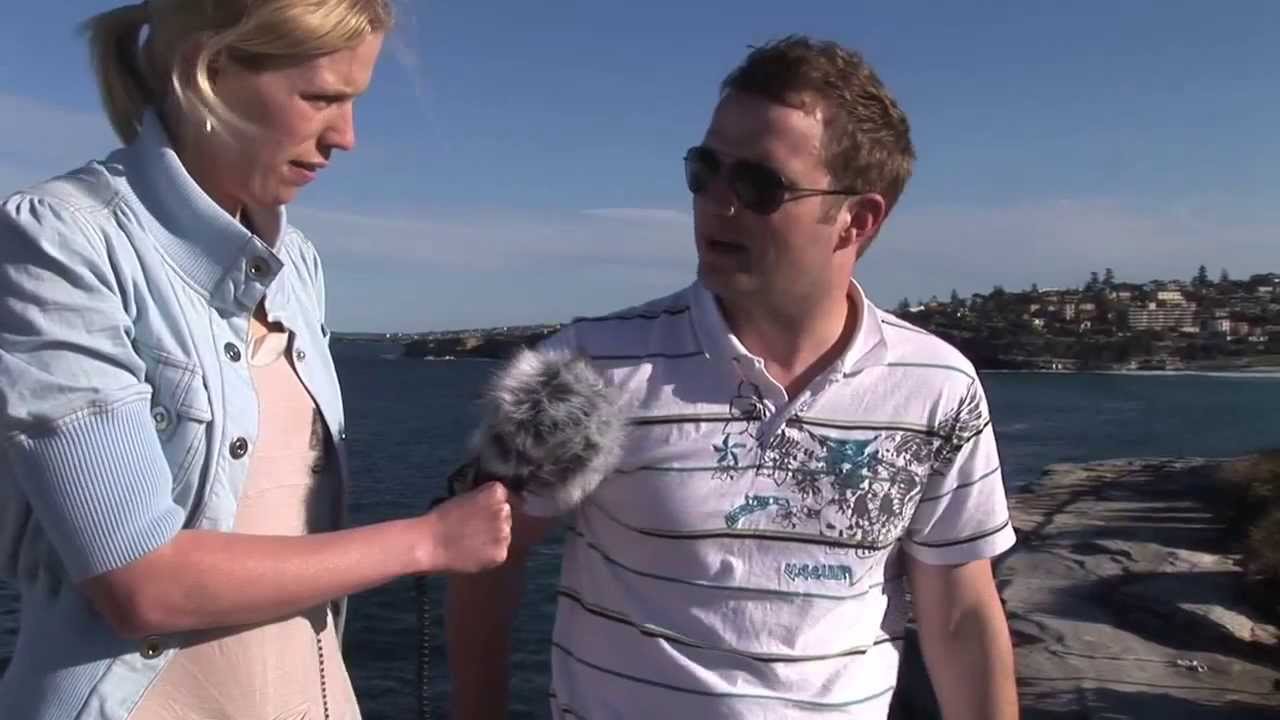
Force is a central concept in physics. By analysing the forces on an object, its resulting motion can be determined. But what exactly is a force? The word force is used in everyday language in a variety of contexts, only some of which reflect the scientific definition of force. In this video, people at Victoria Park in Sydney are interviewed on their ideas of force and the forces that act on them.
In 2020, NASA will send a new rover to the Martian surface with one of its objectives to search for evidence of ancient life on the planet. I made this clip as a correspondent for Bill Nye Saves the World on Netflix.
Touring the Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) in Pasadena was an awesome experience. I didn't think we were going to get into the control room but we got lucky. Some of the greatest moments in the history of space exploration have taken place there. They have a giant vacuum chamber where they can take the rover down to the atmospheric pressure on Mars (roughly .01x Earth's atmosphere) and test all of the devices to make sure there are no electrical discharges due to the reduced pressure. I also enjoyed seeing how the rocks will be cored and stored in tubes and deposited on the Martian surface awaiting pickup by the following mission.
Images courtesy of NASA.
Filmed by Raquel Nuno from 3:30 onwards.
Music: http://epidemicsound.com "Serene Story 2"
Countries are powered by a diverse range of energy sources, but in Australia electricity generation mainly has one source: fossil fuels. Coal, natural gas, and oil account for over 90% of the country's electricity. Hydro provides 7% with only 0.3% provided by wind and solar. Should Australia consider nuclear power? It is a complicated issue leaving many uncertain about its place in Australia's energy future.
JJ Thomson proposed the first model of the atom with subatomic structure. He had performed a series of experiments and was credited with the discovery of the first sub-atomic particle, the electron. He therefore proposed a new model of the atom called the plum pudding model. In this model, the plums represent negatively charged electrons which can be plucked out of the atom, leaving behind some positively charged pudding. In this film, cherry tart is used as a delicious substitute for plum pudding.
How Schlieren imaging works in color, black and white and slow-mo.
Get a free audiobook with a 30 day free trial at http://www.audible.com/veritasium
Special thanks to Patreon supporters:
Tony Fadell, Donal Botkin, Curational, Jeff Straathof, Zach Mueller, Ron Neal, Nathan Hansen, Corvi
Support Veritasium on Patreon: http://ve42.co/patreon
Filming by Raquel Nuno
Sound Effects by A Shell in the Pit
Without neutrons, harnessing nuclear energy would be impossible.
Try Audible free for 30 days: http://audible.com/veritasium
I have a new documentary coming out in a few months - sign up here to be notified and see a sneak preview: http://vitamaniathemovie.com
Special thanks to Patreon supporters:
Tony Fadell, Donal Botkin, Michael Krugman, Jeff Straathof, Zach Mueller, Ron Neal, Nathan Hansen, Yildiz Kabaran,
Terrance Snow
A few years ago I made a documentary about uranium, radioactivity and radiation. I always thought of the characters in our story as the scientists and maybe the uranium nucleus itself. It was only through making the documentary that I realized the real hero of the story is the neutron. Without a neutral nuclear particle, it would be virtually impossible to release the energy from the nucleus. But with it, and the idea of a chain reaction, nuclear energy went from science fiction to reality. That is something I had not grasped as clearly before and it motivated me to make this video.
Filmed by Raquel Nuno.
A basketball and a 5kg medicine ball are dropped simultaneously. Which one hits the ground first? It seems obvious that the heavy one should accelerate at a greater rate and therefore land first because the force pulling it down is greater. But this is forgetting inertia - the tendency of mass to resist changes in motion. Therefore, although the force on the medicine ball is greater, it takes this larger force to accelerate the ball at the same rate as the basketball.
There are a few persistent misconceptions about what causes the seasons. Most believe it is the distance between the Earth and sun which varies to give us seasonal temperature variations. However it is actually the directness of the sun's rays leading to more intense sunshine in summer and less in winter.
Can you predict what happens to the golf ball?
Stays where it is: http://bit.ly/buoyStay
Goes down: http://bit.ly/buoyGoDown
Goes up: http://bit.ly/buoyGoUp
In this experiment we see that a golf ball is denser than detergent (it is also denser than pure water incidentally, which is why water hazards are so effective at ruining a golfer's day on the course). But, a golf ball is less dense than a saturated salt solution. Now the question is: if you pour the detergent on top of the golf ball in the salt solution, what will happen to the golf ball?
Special thanks to Duane Merrell for the idea, which I saw demonstrated at BYU back in February. Thanks to Emil Malmsten for excellent filming, and his Stockholm colleagues who were game to have a chat to me about this experiment.