Top Vídeos
Ultravox perform Sleepwalk on Top of the Pops, 1980.
HD broadcast of SD content.
A couple of these tracks could already be found on youtube - here's the complete thing.
Ultravox! - such a great band while John Foxx was still part of it. They appropriately dropped the '!' afterwards, having become a totally different, utterly boring and ridiculous but -oh the irony of it!- extremely successful combo.
approx.timing :
01 - I want to be a machine - 00.00
02 - Slip away - 06.49
03 - Frozen ones - 11.00
04 - Distant smile - 15.22
05 - Young savage - 18.46
06 - My sex - 22.14
07 - Artificial life - 25.08 (fades in)
08 - Wide boys - 29.50
09 - Saturday night (in the city of the dead) - 32.38
10 - The wild, the beautiful and the damned - 35.35
11 - Rockwrok - 42.02
12 - Fear in the western world - 45.25 (incomplete - fades out)
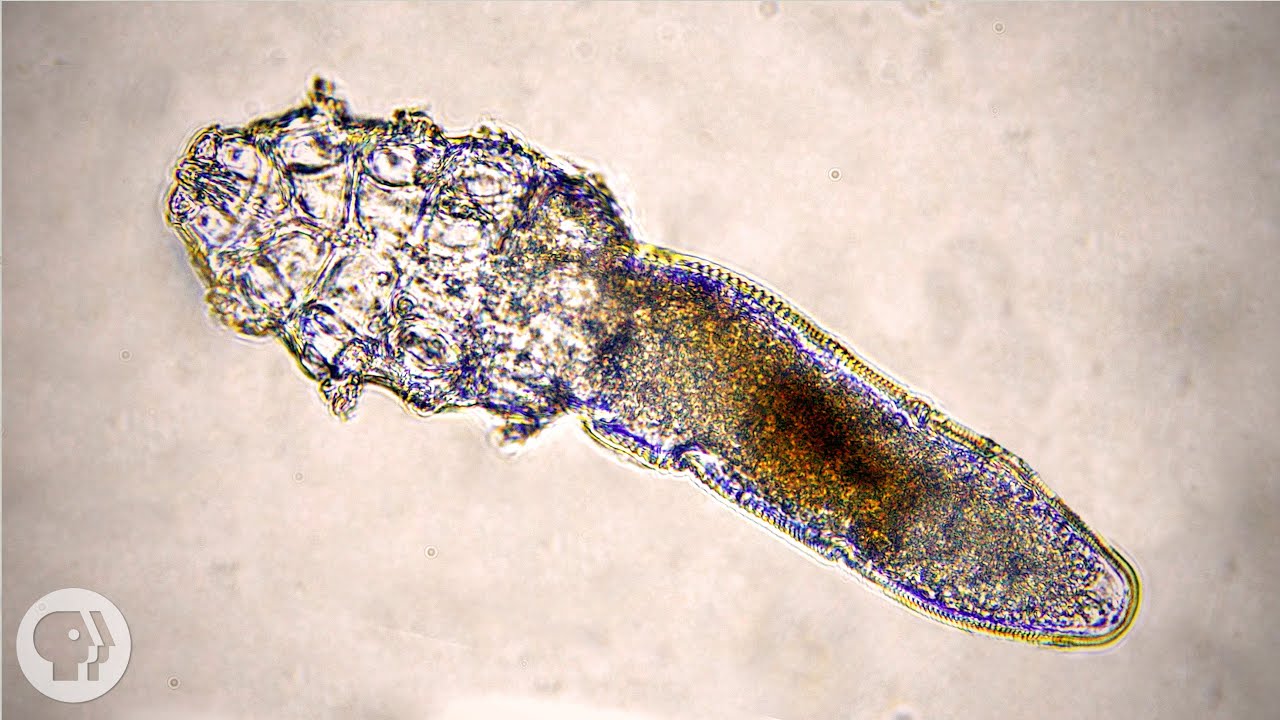
Yep, you probably have Demodex mites living on your face. These tiny arachnids feast on sebum, the greasy oil in your pores. But should you be worried about your eight-legged guests?
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
Please support us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
DEEP LOOK is a ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
Pretty much every adult human alive has a population of these mites living on them.
Also called eyelash mites, they’re too small to see with the naked eye. They’re mostly transparent, and at about .3 millimeters long, it would take about five face adult mites laid end to end to stretch across the head of a pin.
Face mites spend their days face-down inside your hair follicles nestled up against the hair shaft.
They eat sebum, that greasy oil your skin makes to protect itself and keep it from drying out. That’s why the greasiest parts of your body — like around the eyes, nose and mouth — likely harbor a higher concentration of mites than other areas.
They live about two weeks. They spend most of their time tucked inside our pores. But while we’re sleeping, they crawl out onto the surface of our skin to mate before crawling back into our pores to lay their eggs. Fun!
--- How common are face mites?
Pretty much everyone has some face mites on them. Babies are born without them but quickly receive them from their parents through direct contact. The amount of mites may increase during puberty when the skin starts to produce more oil.
--- How do you get rid of face mites?
There’s usually no need to try to rid yourself of face mites as they typically don’t cause any symptoms and are nearly impossible to fully eradicate. Since female face mites can also reproduce asexually, it only takes one mite to repopulate your skin. Some people experience an overpopulation of face mites resulting in an inflammatory disease called demodicosis which is easy to recognize sue to the many small evenly-sized pimples that appear quickly. Consult a dermatologist if you think you may have symptoms.
--- What do face mites eat?
Face mites consume the greasy oil that you skin produces to protect itself.
---+ Read the entire article on KQED
https://www.kqed.org/science/1....941506/these-face-mi
---+ More Great Deep Look episodes:
How Lice Turn Your Hair Into Their Jungle Gym | Deep Look
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yb26BBvAAWU&t=1s
How Ticks Dig In With a Mouth Full of Hooks | Deep Look
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_IoOJu2_FKE
---+ Shoutout!
?Congratulations? to jac lyn, Vanessa C u later, aspireme_95, Émile Julien, and Nono Chan who correctly identified the part of this animal that is, well… missing. Demodex lack an anus! Se the Community Tab post here: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UC-3SbfTPJsL8fJAPK
---+ Thank you to our Top Patreon Supporters ($10+ per month)!
Ahegao Comics, Allen, Aurora Mitchell, Beckie, Ben Espey, Bill Cass, Breanna Tarnawsky, Carlos Zepeda, Chris B Emrick, Chris Murphy, Companion Cube, Cooper Caraway, Daisuke Goto, Daniel Weinstein, David Deshpande, Edwin Rivas, Elizabeth Ann Ditz, Elizabeth Wolden, Ivan Alexander, Iver Soto, Jane Orbuch, JanetFromAnotherPlanet, Jason Buberel, Jeanine Womble, Jenn's Bowtique, Jeremy Lambert, Jiayang Li, Joao Ascensao, johanna reis, Johnnyonnyful, Joshua Murallon Robertson, Justin Bull, Karen Reynolds, Kristell Esquivel , KW, Kyle Fisher, Laurel Przybylski, Levi Cai, Lyall Talarico, Mario Rahmani, Marjorie D Miller, Mark Joshua Bernardo, Michael Mieczkowski, Monica Albe, Nathan Padilla, Nathan Wright, Pamela Parker, PM Daeley, Ricardo Martinez, Robert Amling, Robert Warner, Sayantan Dasgupta, Sean Tucker, Shelley Pearson Cranshaw, Shirley Washburn, SueEllen McCann, Tatianna Bartlett, Tea Torvinen, TierZoo, Tommy Tran, Two Box Fish, WhatzGames, Willy Nursalim
---+ Follow KQED Science and Deep Look:
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/kqedscience/
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
KQED Science on kqed.org: http://www.kqed.org/science
Facebook Watch: https://www.facebook.com/DeepLookPBS/
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate in San Francisco, CA, serves Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial TV, Radio and web media.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is also supported by the National Science Foundation, the Templeton Religion Trust, the Templeton World Charity Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Fuhs Family Foundation and the members of KQED.
#facemites #demodex #deeplook
Pollinator. Mason. Jeweler. A female blue orchard bee is a multitasking master. She fashions exquisite nests out of mud and pollen that resemble pieces of jewelry. And in the process, she helps us grow nuts and fruits.
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
Please support us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
The PBSDS survey is now close - thanks!
DEEP LOOK is a ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Get a new perspective on our place in the universe and explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
* NEW VIDEOS EVERY OTHER TUESDAY! *
A new type of bee is buzzing through California's orchards. And researchers are hoping that the iridescent, greenish insect may help provide a more efficient way to pollinate nuts and fruits in an era when traditional honeybees have struggled.
Unlike honeybees, blue orchard bees don’t sting humans. And instead of building large colonies with thousands of worker bees caring for eggs laid by a queen bee, female blue orchard bees work alone to build their nests and stock them with food. They’re solitary bees, like most of the 4,000 species of bees in North America.
Blue orchard bees, which are native to the United States, are of increasing interest to scientists, government agencies and farmers for their ability to pollinate almonds, sweet cherries and other tree fruits more efficiently than honeybees.
“This is, I think, the moment for these bees to shine,” said entomologist Natalie Boyle, who studies blue orchard bees at the United States Department of Agriculture in Logan, Utah.
Boyle works with almond growers in California, whose crop is worth $5.2 billion a year and who rely heavily on honeybees to pollinate their orchards every February. Research has found that 400 female blue orchard bees are as effective at pollinating almonds as the more than 10,000 bees in a honeybee hive, said Boyle.
Between 40 and 50 percent of honeybee colonies die each year around the country, according to the yearly National Honey Bee Survey, carried out by universities with the sponsorship of the USDA and the California Almond Board, among others.
Finding other bees that could work side by side with honeybees could offer what Boyle calls “pollination insurance.”
--- What is a mason bee?
The blue orchard bee is a mason bee. Females build their nests out of mud that they collect with two huge pincer-like tools on their face called mandibles. In nature, they build their nests in places like hollow twigs. But they will also build them in pencil-wide drill holes in a wood block.
--- What makes blue orchard bees good pollinators?
One thing that makes blue orchard bees good pollinators are hairs on their abdomen called scopa, on which they collect and spread pollen. Blue orchard bees are particularly good at pollinating almonds and tree fruits like cherries and apples because they love foraging in their flowers. And they’re particularly well-suited to pollinate almonds, which are in bloom in February, when it’s chilly in California’s Central Valley, because they will fly around and forage at a cooler temperature than honeybees.
---+ Read the article on KQED Science:
https://www.kqed.org/science/1....928378/watch-this-be
---+ For more information:
Download the free book How to Manage the Blue Orchard Bee:
https://www.sare.org/Learning-....Center/Books/How-to-
---+ More Great Deep Look episodes:
This Vibrating Bumblebee Unlocks a Flower’s Hidden Treasure
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SZrTndD1H10
What Do Earwigs Do With Those Pincers Anyway?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HuOnqWpIL9E
---+ See some great videos and documentaries from PBS Digital Studios!
PBS Eons: When Insects First Flew
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7QMcXEj7IT0
CrashCourse: The Plants & The Bees: Plant Reproduction - CrashCourse Biology #38
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ExaQ8shhkw8
---+ Follow KQED Science:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/kqedscience/
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
KQED Science on kqed.org: http://www.kqed.org/science
Facebook Watch: https://www.facebook.com/DeepLookPBS/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate in San Francisco, CA, serves Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial TV, radio and web media.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is supported by the Templeton Religion Trust and the Templeton World Charity Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Fuhs Family Foundation Fund and the members of KQED.
#deeplook #blueorchardbee #wildlifedocumentary
There's a story in every grain of sand: tales of life and death, fire and water. If you scooped up a handful of sand from every beach, you'd have a history of the world sifting through your fingers.
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK: a new ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Get a new perspective on our place in the universe and meet extraordinary new friends. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
* NEW VIDEOS EVERY OTHER TUESDAY! *
---+ How does sand form?
Sand can be anything that has been worn down until it’s reduced to some tiny, essential fragment of what it once was: a granite pebble from the mountains; coral from the sea; obsidian from a volcano; even skeletons of microscopic sea animals. It's also a technical term. Bigger than sand, that’s gravel, smaller? Silt.
By studying the composition and texture of sand, geologists can reconstruct its incredible life history. “There’s just a ton of information out there, and all of it is in the sand,” said Mary McGann, a geologist at the United States Geological Survey in Menlo Park, CA.
McGann recently took part in a comprehensive research project mapping sand’s journey into and throughout San Francisco Bay.
Patrick Barnard, another USGS geologist who helped oversee the project, said that it will help scientists understand how local beaches are changing over time. In particular, Barnard wants to understand why beaches just south of San Francisco Bay are among the most rapidly eroding beaches in the state.
From 2010-2012, Barnard and his team sampled beaches, outcrops, rivers and creeks to track sand’s journey around the bay. They even collected sand from the ocean floor. The researchers then carefully analyzed the samples to characterize the shapes, sizes, and chemical properties of the sand grains.
Barnard said the information provides a kind of fingerprint, or signature, for each sample that can then be matched to a potential source. For example, certain minerals may only come from the Sierra Mountains or the Marin Headlands.
“If we’ve covered all of the potential sources, and we know the unique signature of the sand from these different sources, and we find it on a beach somewhere, then we basically know where it came from,” explained Barnard.
And those species aren’t the only things finding their way into the sand. Manmade materials can show up there, too. McGann has found metal welding scraps and tiny glass spheres (commonly sprinkled on highways to make road stripes reflective) in sand samples from around the bay.
“All of these things can get washed into our rivers or our creeks, or washed off the road in storm drains,” explained McGann. “Eventually they end up in, for example, San Francisco Bay.”
By piecing together all of these clues – the information found in the minerals, biological material and man made objects that make up sand – the researchers ended up with a pretty clear picture of how sand travels around San Francisco Bay.
Some sands stay close to home. Rocky sand in the Marin Headlands comes from nearby bluffs, never straying far from its source.
Other sands travel hundreds of miles. Granite from the Sierra Nevada mountains careens down rivers and streams on a century-long sojourn to the coast.
In fact, much of the sand in the Bay Area comes from the Sacramento and San Joaquin rivers, with local watersheds also playing an important role in transporting sand to the beach.
Although this project focused on San Francisco Bay, the same techniques could be used to study other coastal systems, he added, revealing the incredible life stories of sand from around the world.
---+ More Deep Look episodes:
What Happens When You Zap Coral With The World's Most Powerful X-ray Laser?
https://youtu.be/aXmCU6IYnsA
These 'Resurrection Plants' Spring Back to Life in Seconds
https://youtu.be/eoFGKlZMo2g
--
Full article: http://blogs.kqed.org/science/....2014/11/04/the-amazi
---+ Follow KQED Science:
KQED Science: http://www.kqed.org/science
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate in San Francisco, CA, serves Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial TV, Radio and web media.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios and the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is also supported by HopeLab, the David B. Gold Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Smart Family Foundation and the members of KQED.
#deeplook
Support Deep Look on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
A baby hairworm hitches a ride inside a cricket, feasting on its fat until the coiled-up parasite is ready to burst out. Then it hijacks the cricket's mind and compels it to head to water for a gruesome little swim.
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK is an ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
If you’re out on a hike and look down at a puddle, you might spot a long, brown spaghetti-shaped creature whipping around madly in a figure 8.
It’s a hairworm – also known as a horsehair worm or Gordian worm – and researchers have described 350 species around the world. Good news: It isn’t interested in infecting or attacking humans. But if you had happened on the puddle a few hours earlier, you might have witnessed a gruesome spectacle – the hairworm wriggling out of a cricket’s body, pushing its way out like the baby monster in the movie “Alien.”
How a hairworm ends up in a puddle, or another water source such as a stream, hot tub or a pet’s water dish, is a complex story. A young hairworm finds its way into a cricket or similar insect like a beetle or grasshopper, and once it’s grown into an adult, the parasite takes over its host’s brain to hitch a ride to the water.
As a result of the infection, crickets stop growing and reproducing. Male crickets infected by hairworms even lose their chirp, said Ben Hanelt, a biologist at the University of New Mexico who studies hairworms.
--- What *is* a hair worm?
A hair worm or hairworm – pick your spelling – is a nematomorph. Nematomorpha are a group of parasites. They’re long, thin worms that can grow to be several meters long inside their host.
--- Can humans be infected by hair worms?
There are reports of humans and cats and dogs being infected by hair worms, but hair worms aren’t after us or our pets because they can’t grow inside us, said Hanelt. They can only grow inside a host like a cricket or a related insect.
“What happens is that a dog, a cat, a human will ingest an adult (hair worm) somehow,” said Hanelt. “Could a cricket crawl in your sandwich before you take a bite? I don’t know. None of the studies that are out there talk about that. What they have been reported to do is to cause in many people intestinal distress.”
--- How do hair worms control crickets’ minds?
Scientists don’t understand the precise mechanism yet, but they believe that hairworms either boost chemicals in the crickets’ brains or pump chemicals into their brains.
---+ Read the entire article on KQED Science:
https://www.kqed.org/science/1....937775/these-hairwor
---+ For more information:
Hairworm Biodiversity Survey: http://www.nematomorpha.net
---+ More great Deep Look episodes:
Jerusalem Crickets Only Date Drummers
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mHbwC-AIyTE
How Mosquitoes Use Six Needles to Suck Your Blood
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rD8SmacBUcU
Identical Snowflakes? Scientist Ruins Winter For Everyone
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gojddrb70N8
---+ Follow KQED Science:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/kqedscience/
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
KQED Science on kqed.org: http://www.kqed.org/science
Facebook Watch: https://www.facebook.com/DeepLookPBS/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
---+ Shoutout!
?Congratulations ? to Sushant Mendon who won our GIF CHALLENGE over at the Deep Look Community Tab: https://www.youtube.com/user/K....QEDDeepLook/communit
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate in San Francisco, CA, serves Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial TV, radio and web media.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is also supported by the National Science Foundation, the Templeton Religion Trust, the Templeton World Charity Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Fuhs Family Foundation and the members of KQED. #deeplook #hairworms #wildlife
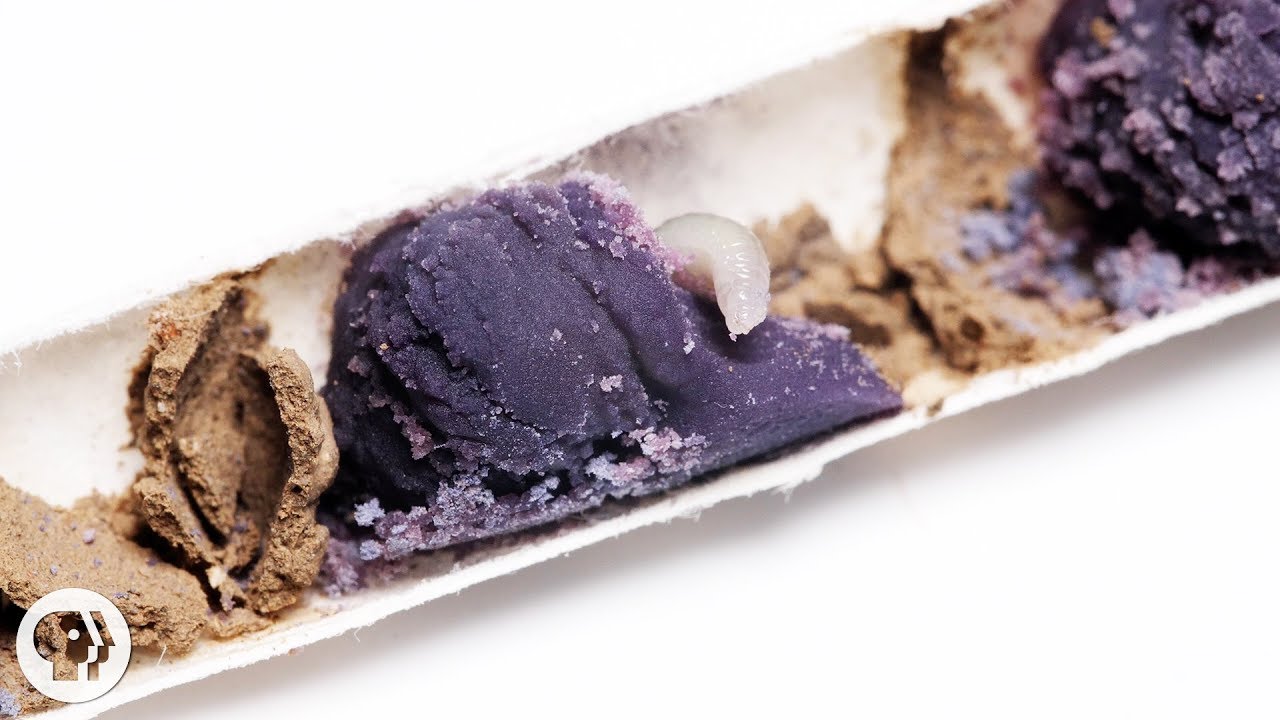
Plenty of animals build their homes in oak trees. But some very teeny, tricky wasps make the tree do all the work. And each miniature mansion the trees build for the wasps' larvae is weirder and more flamboyant than the next.
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK: a ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Get a new perspective on our place in the universe and meet extraordinary new friends. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
* NEW VIDEOS EVERY OTHER TUESDAY! *
“What nerve!” you might say. What… gall! And you’d be right. The wasps are called gall-inducers.
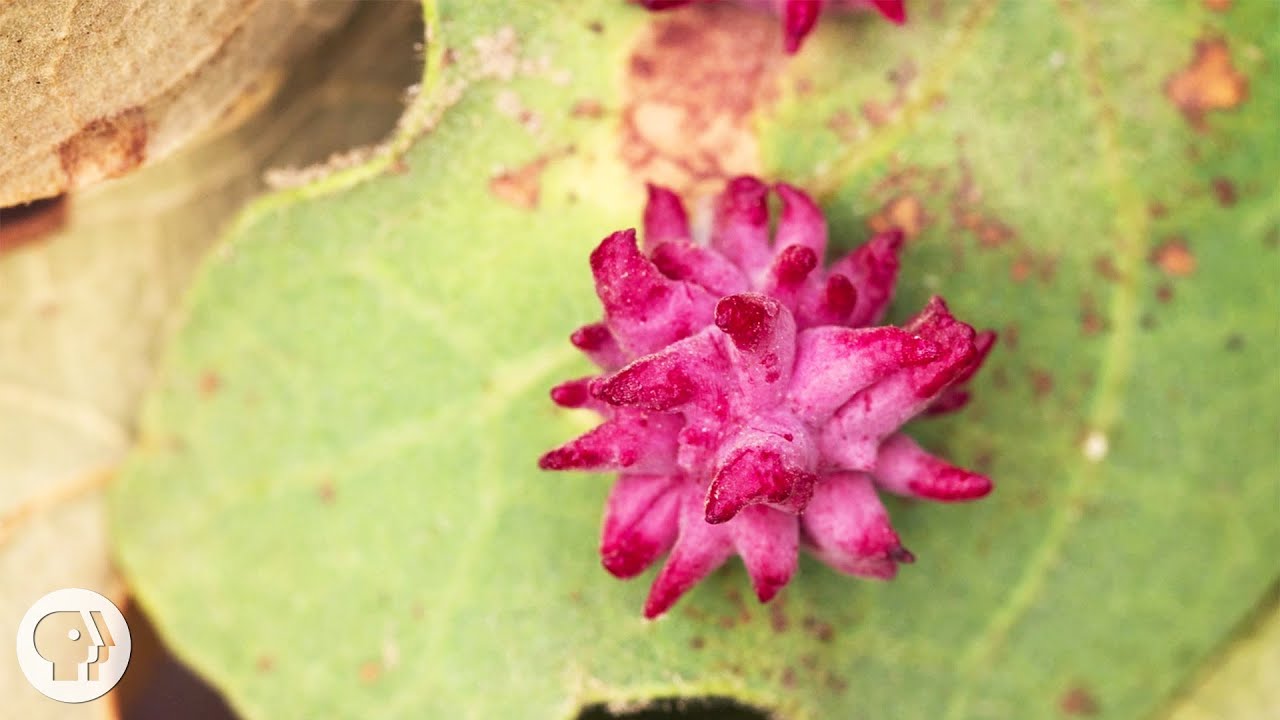
---+ What do oak galls look like?
If you’ve ever spent a Summer or Fall around oak trees – such as the stalwart Valley Oak – Quercus lobata, or the stately Blue Oak, Quercus douglasii – you may be familiar with the large, vaguely fruity-looking objects clinging to the branches and leaves. Commonly called oak apples, these growths are the last thing you’d want to put in your mouth. They are intensely bitter, loaded with tannin compounds – the same compounds that in modest amounts give red wine its pleasant dryness, and tea its refreshing earthy tang.
That said, the oak apple’s powerful astringency has been prized for millennia. Tanning leather, making ink or dye, and cleaning wounds have been but a few of the gall’s historical uses.
But on closer inspection of these oaks – and many other plants and trees such as willows, alders, manzanitas, or pines – you can find a rogue’s gallery of smaller galls. Carefully peeking under leaves, along the stems and branches, or around the flower buds and acorns will likely lead you to unexpected finds. Smooth ones. Spiky ones. Long skinny ones, flat ones, lumpy, boxy ones. From the size of a golf ball down to that of a poppy seed. These structures wear shades of yellow, green, brown, purple, pink and red – and sometimes all of the above. A single tree may be host to dozens of types of gall, each one caused by a specific organism. And their shapes range from the sublime to the downright creepy. One tree may be encrusted with them, like a Christmas tree laden with ornaments and tinsel; and the next tree over may be almost completely free of galls. Why? It’s a mystery.
---+ How do oak galls form?
Galls are generally formed when an insect, or its larvae, introduce chemicals into a specific location, to push the plant’s growth hormones into overdrive. This can result in a great profusion of normal cells, increased size of existing cells, or the alteration of entire plant structures into new, alien forms.
Lots of creatures cause them; midges, mites, aphids, flies, even bacteria and viruses. But the undisputed champs are a big family of little wasps called Cynipids– rarely exceeding the size of a mosquito, a quarter of an inch in length.
“These tiny wasps cannot sting,” says Dr. Kathy Schick, Assistant Specialist/Curatorial Assistant at the Essig Museum of Entomology at UC Berkeley. “Gall-inducers are fascinating in that they are very specialized to their organ of the host plant.”
---+ What are oak galls?
These wasp houses are not homes exactly, but more akin to nurseries. The galls serve as an ideal environment for wasp larvae, whether it is a single offspring, or dozens. The tree is tricked into generating outsize amounts of soft, pillowy tissue inside each gall, on which the larvae gladly gorge themselves as they grow.
Full article: http://blogs.kqed.org/science/....2014/11/18/what-gall
---+ See more great videos and documentaries from the PBS Digital Studios!
It's Okay to Be Smart: Inside the World of Fire Ants!
https://youtu.be/rz3UdLEWQ60
Gross Science: Can Spider Venom Cure Erectile Dysfunction?
https://youtu.be/5i9X8h17VNM
---+ More Great Deep Look episodes:
These Lizards Have Been Playing Rock-Paper-Scissors for 15 Million Years
https://youtu.be/rafdHxBwIbQ
Stinging Scorpion vs. Pain-Defying Mouse
https://youtu.be/w-K_YtWqMro
---+ Follow KQED Science:
KQED Science: http://www.kqed.org/science
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate in San Francisco, CA, serves Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial TV, Radio and web media.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios and the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is also supported by HopeLab, the David B. Gold Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Smart Family Foundation and the members of KQED.
#deeplook
Their skeletons are prized by beachcombers, but sand dollars look way different in their lives beneath the waves. Covered in thousands of purple spines, they have a bizarre diet that helps them exploit the turbulent waters of the sandy sea floor.
Please follow us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK is a ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
Pristine white sand dollars have long been the souvenir to commemorate a successful day at the beach. But most people who pick them up don’t realize that they’ve collected the skeleton of an animal, washed up at the end of a long life.
As it turns out, scientists say there’s a lot to be said about a sand dollar’s life. That skeleton -- also known as a test -- is really a tool, a remarkable feat of engineering that allows sand dollars to thrive on the shifting bottom of the sandy seafloor, an environment that most other sea creatures find inhospitable.
“They've done something really amazing and different,” said Rich Mooi, a researcher with the California Academy of Sciences in San Francisco. “They’re a pile of novelties, and they’ve gone way off the deep end in modifying their bodies to adapt to where they live.”
Mooi studies echinoderms, a word that roughly translates to “hedgehog skin.” It’s an aptly-fitting name for a group that includes sea urchins, sand dollars, sea stars and sea cucumbers. But Mooi says sand dollars really have his heart, in part because of their incredible adaptations.
--- What are sand dollars?
Sand dollars belong to a group of animals called Echinoderms that includes some more familiar animals like starfish and sea urchins. Sand dollars are actually a type of flattened sea urchin with miniaturized spines and tube feet more suited to sandy seafloors.
--- What do sand dollars eat?
Sand dollars consume sand but they get actual nutrition from the layer of algae and bacteria that coat the grains, not the sand itself.
--- Are sand dollars alive? Why do they Turn White?
When sand dollars are alive, they are covered in tiny tube feet and spines that make them appear like fuzzy discs. When they die, they lose their spines and tube feet exposing their white skeleton that scientists call a test. That skeleton is typically what people find on the beach.
---+ Read the entire article on KQED Science:
https://www.kqed.org/science/1....932072/a-sand-dollar
---+ For more information:
Learn more about Chris Lowe’s work with plankton including sand dollars and their relatives
http://lowe.stanford.edu/
Rich Mooi’s research into sand dollars for California Academy of Sciences
https://www.calacademy.org/lea....rn-explore/science-h
---+ More Great Deep Look episodes:
The Amazing Life of Sand | Deep Look
https://youtu.be/VkrQ9QuKprE
For Pacific Mole Crabs It's Dig or Die | Deep Look
https://youtu.be/tfoYD8pAsMw
This Adorable Sea Slug is a Sneaky Little Thief | Deep Look
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KLVfWKxtfow&t=112s
---+ See some great videos and documentaries from PBS Digital Studios!
These Tiny Cells Shape Your Life | BrainCraft
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fnx-Qvx_fA8
What are Eye Boogers? | Reactions
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w3M8p-QCC7I
---+ Follow KQED Science:
KQED Science: http://www.kqed.org/science
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate in San Francisco, CA, serves Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial TV, Radio and web media.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is supported by the Templeton Religion Trust and the Templeton World Charity Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Fuhs Family Foundation Fund and the members of KQED.
---+ SHOUT OUTS
Here are the winners from our episode image quiz posted in our channel Community Tab:
https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UC-3SbfTPJsL8fJAPK
?#1: Tektyx
Was the first to correctly ID the creature in our episode was a sand dollar.
?#2: tichu7
Was the first to ID what kind of sand dollar it was, the Pacific sand dollar.
?#3: Miguel Gomez
Also posted what kind of sand dollar it was was, but by another name: Eccentric sand dollar.
?#4: Gir Gremlin
The first viewer to identify the sand dollar by its scientific name: Dendraster excentricus!
Male side-blotched lizards have more than one way to get the girl. Orange males are bullies. Yellows are sneaks. Blues team up with a buddy to protect their territories. Who wins? It depends - on a genetic game of roshambo.
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK is a ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Get a new perspective on our place in the universe. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
* NEW VIDEOS EVERY OTHER TUESDAY! *
Every spring, keen-eyed biologists carrying fishing poles search the rolling hills near Los Banos, about two hours south of San Francisco. But they’re not looking for fish. They’re catching rock-paper-scissors lizards.
The research team collects Western side-blotched lizards, which come in different shades of blue, orange and yellow.
Barry Sinervo, a professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at UC Santa Cruz, leads the team. Their intricate mating strategies reminded the the researchers of the rock-paper-scissors game where rock beats scissors, scissors beats paper and paper beats rock.
It’s all about territories. Orange males tend to be the biggest and most aggressive. They hold large territories with several females each and are able to oust the somewhat smaller and less aggressive blues. Blue males typically hold smaller territories and more monogamous, each focusing his interest on a single female. Yellow males tend not to even form exclusive territories Instead they use stealth to find unaccompanied females with whom to mate.
The yellow males are particularly successful with females that live in territories held by their more aggressive orange competitors. Because the orange males spread their attention among several females, they aren’t able to guard each individual female against intruding yellow males. But the more monogamous blues males are more vigilant and chase sneaky yellow males away.
Their different strategies keep each other in check making the system stable. Sinervo believes this game has likely been in play for at least 15 million years.
--- How do side-blotched lizards choose a mate?
The males compete with each other, sometimes violently, for access to females. The females generally prefer males of their own color but also give preference to whichever color male is more rare that mating season.
--- Why do lizards do push up and down?
Male lizards do little pushups as a territorial display meant to tell competitors to back off. It’s best to use a warning instead of fighting right away because there’s always a danger of getting hurt in a fight. Some lizards like side-blotched lizards also use slow push ups to warn their neighbors of an incoming threat.
--- Why do side-blotched lizards fight?
Sometimes aggressive territorial displays are not enough to dissuade invaders so side-blotched lizards will resort to fighting. They have small sharp teeth and will lunge at each other inflicting bites and headbutts.
---+ Read the entire article on KQED Science: https://ww2.kqed.org/science/2....016/05/17/these-liza
---+ For more information:
The Lab of Dr. Barry Sinervo, LizardLand, University of California, Santa Cruz http://bio.research.ucsc.edu/~....barrylab/lizardland/
---+ More Great Deep Look episodes:
Meet the Dust Mites, Tiny Roommates That Feast On Your Skin
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ACrLMtPyRM0
Stinging Scorpion vs. Pain-Defying Mouse
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w-K_YtWqMro
These Crazy Cute Baby Turtles Want Their Lake Back
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YTYFdpNpkMY
---+ See some great videos and documentaries from the PBS Digital Studios!
It's Okay to Be Smart: The Cosmic Afterglow
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZvrHL7-c1Ys
It's Okay to Be Smart: The Most Important Moment in the History of Life
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Jf06MlX8yik
---+ Follow KQED Science:
KQED Science: http://www.kqed.org/science
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate based in San Francisco, serves the people of Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial media. KQED is also a leader and innovator in interactive media and technology, taking people of all ages on journeys of exploration — exposing them to new people, places and ideas.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios and the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is also supported by HopeLab, the David B. Gold Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Smart Family Foundation and the members of KQED.
#deeplook #lizards #rockpaperscissorslizardspock
Pacific mole crabs, also known as sand crabs, make their living just under the surface of the sand, where they're safe from breaking waves and hungry birds. Some very special physics help them dig with astonishing speed.
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK is a ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Get a new perspective on our place in the universe. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
* NEW VIDEOS EVERY OTHER TUESDAY! *
Among the surfers and beach-casting anglers, there’s a new visitor to San Francisco’s Ocean Beach shoreline.
Benjamin McInroe is there for only one reason -- to find Pacific mole crabs, a creature commonly known as “sand crabs” -- and the tiny animals whose burrowing causes millions of small bubbles to appear on the beach as the tide comes in and out.
McInroe is a graduate student from UC Berkeley studying biophysics. He wants to know what makes these little creatures so proficient at digging their way through the wet sand.
McInroe hopes that he can one day copy their techniques to build a new generation of digging robots.
-- What are Pacific Mole Crabs?
Pacific mole crabs, also known as sand crabs, are crustaceans, related to shrimp and lobsters. They have four pairs of legs and one pair of specialized legs in the front called uropods that look like paddles for digging in sand. Pacific mole crabs burrow through wet sand and stick their antennae out to catch bits of kelp and other debris kicked up by the breaking waves.
-- What makes those holes in the sand at the beach?
When the waves recede, mole crabs burrow down into the sand to keep from being exposed. They dig tail-first very quickly leaving holes in the wet sand. The holes bubble as water seeps into the holes and the air escapes.
-- What do birds eat in the wet beach sand?
Shore birds like seagulls rush down the beach as the waves recede to catch mole crabs that haven’t burrowed down quickly enough to escape. The birds typically run or fly away as the next wave breaks and rolls in.
---+ Read the entire article on KQED Science:
https://ww2.kqed.org/science/2....018/02/13/for-pacifi
---+ For more information:
Benjamin McInroe, a Ph.D. student at UC Berkeley, studies how Pacific mole crabs burrow
https://www.ocf.berkeley.edu/~bmcinroe/
Professor Robert Full directs the Poly-PEDAL Lab at UC Berkeley, where researchers study the physics of how animals and use that knowledge to build mechanical systems like robots based on their findings.
http://polypedal.berkeley.edu/
---+ More Great Deep Look episodes:
Decorator Crabs Make High Fashion at Low Tide | Deep Look
https://youtu.be/OwQcv7TyX04
These Fish Are All About Sex on the Beach | Deep Look
https://youtu.be/j5F3z1iP0Ic
Sea Urchins Pull Themselves Inside Out to be Reborn | Deep Look
https://youtu.be/ak2xqH5h0YY
There's Something Very Fishy About These Trees ... | Deep Look
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rZWiWh5acbE&t=1s
---+ See some great videos and documentaries from the PBS Digital Studios!
Why Do We Eat Artificial Flavors? | Origin of Everything
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iNaJ31EV13U
The Facts About Dinosaurs & Feathers
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aOeFRg_1_Yg
Why Is Blue So Rare In Nature?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3g246c6Bv58
---+ Follow KQED Science
KQED Science: http://www.kqed.org/science
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate in San Francisco, CA, serves Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial TV, Radio and web media.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is supported by the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Fuhs Family Foundation Fund and the members of KQED.
#deeplook
Honey bees make honey from nectar to fuel their flight – and our sweet tooth. But they also need pollen for protein. So they trap, brush and pack it into baskets on their legs to make a special food called bee bread.
JOIN our Deep Look community on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK is a ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
Spring means honey bees flitting from flower to flower. This frantic insect activity is essential to growing foods like almonds, raspberries and apples. Bees move pollen, making it possible for plants to grow the fruit and seeds they need to reproduce.
But honey bees don’t just move pollen from plant to plant. They also keep a lot for themselves. They carry it around in neat little balls, one on each of their hind legs. Collecting, packing and making pollen into something they can eat is a tough, intricate job that’s essential to the colony’s well-being.
Older female adult bees collect pollen and mix it with nectar or honey as they go along, then carry it back to the hive and deposit it in cells next to the developing baby bees, called larvae. This stored pollen, known as bee bread, is the colony’s main source of protein.
“You don’t have bees flying along snacking on pollen as they’re collecting it,” said Mark Carroll, an entomologist at the US Department of Agriculture’s Carl Hayden Bee Research Center in Tucson. “This is the form of pollen that bees are eating.”
--- What is bee bread?
It’s the pollen that worker honey bees have collected, mixed with a little nectar or honey and stored within cells in the hive.
--- What is bee bread used for?
Bee bread is the main source of protein for adult bees and larvae. Young adult bees eat bee bread to make a liquid food similar to mammal’s milk that they feed to growing larvae; they also feed little bits of bee bread to older larvae.
--- How do honey bees use their pollen basket?
When a bee lands on a flower, it nibbles and licks off the pollen, which sticks to its head. It wipes the pollen off its eyes and antennae with a brush on each of its front legs, using them in tandem like windshield wipers. It also cleans the pollen off its mouth part, and as it does this, it mixes it with some saliva and a little nectar or honey that it carries around in a kind of stomach called a crop.
Then the bee uses brushes on its front, middle and hind legs to move the pollen, conveyor-belt style, front to middle to back. As it flies from bloom to bloom, the bee combs the pollen very quickly and moves it into baskets on its hind legs. Each pollen basket, called a corbicula, is a concave section of the hind leg covered by longish hairs that bend over and around the pollen.
---+ Read the entire article on KQED Science:
https://www.kqed.org/science/1....940898/honey-bees-ma
---+ Shoutout!
?Congratulations ?to spqr0a, A D2, James Peirce, Armageddonchampion, and Даниил Мерзликин for identifying what our worker bee was putting in a honeycomb cell (and why) - Bee Bread! See more on our Community Tab: https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UC-3SbfTPJsL8fJAPK
---+ Thank you to our Top Patreon Supporters ($10+ per month)!
Ahegao Comics, Allen, Aurora Mitchell, Beckie, Ben Espey, Bill Cass, Breanna Tarnawsky, Carlos Zepeda, Chris B Emrick, Chris Murphy, Companion Cube, Cooper Caraway, Daisuke Goto, Daniel Weinstein, David Deshpande, Edwin Rivas, Elizabeth Ann Ditz, Elizabeth Wolden, Ivan Alexander, Iver Soto, Jane Orbuch, JanetFromAnotherPlanet, Jason Buberel, Jeanine Womble, Jenn's Bowtique, Jeremy Lambert, Jiayang Li, Joao Ascensao, johanna reis, Johnnyonnyful, Joshua Murallon Robertson, Justin Bull, Karen Reynolds, Kristell Esquivel , KW, Kyle Fisher, Laurel Przybylski, Levi Cai, Lyall Talarico, Mario Rahmani, Marjorie D Miller, Mark Joshua Bernardo, Michael Mieczkowski, Monica Albe, Nathan Padilla, Nathan Wright, Pamela Parker, PM Daeley, Ricardo Martinez, Robert Amling, Robert Warner, Sayantan Dasgupta, Sean Tucker, Shelley Pearson Cranshaw, Shirley Washburn, SueEllen McCann, Tatianna Bartlett, Tea Torvinen, TierZoo, Tommy Tran, Two Box Fish, WhatzGames, Willy Nursalim
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate in San Francisco, CA, serves Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial TV, radio and web media.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is also supported by the National Science Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Fuhs Family Foundation, Campaign 21 and the members of KQED. #honeybees #bee bread #deeplook
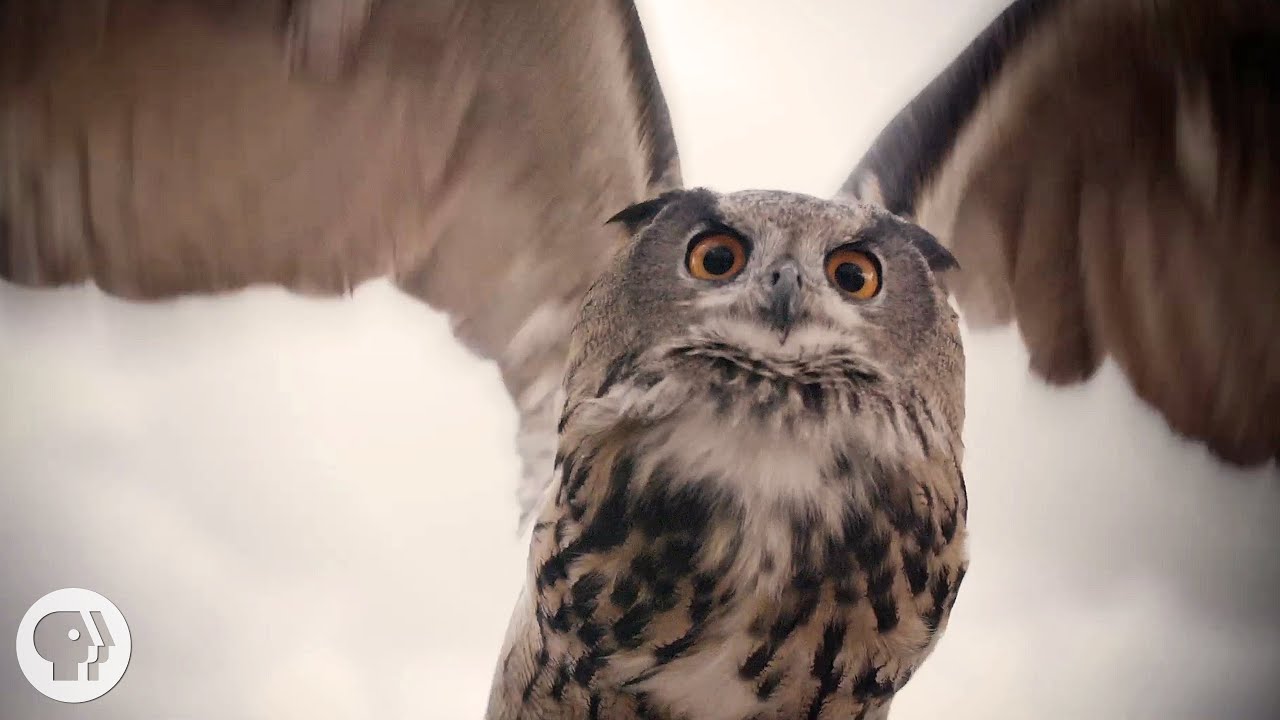
It's stealth, not speed that makes owls such exceptional hunters. Zoom way in on their phenomenal feathers to see what makes them whisper-quiet.
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK: a new ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Get a new perspective on our place in the universe and meet extraordinary new friends. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
--- How do owls hunt silently?
When birds flap their wings it creates turbulences in the air as it rushes over their wings. In general, the larger a bird is and the faster it flies, the larger the turbulence created and that means more sound.
The feathers at the leading edge of an owl’s wings have an unusual serrated appearance, referred to as a comb or fringe. The tiny hooked projections stick out and break up the wind as it flows over the owl’s wings reducing the size and sound of the turbulences.
Owl feathers go one step further to control sound. When viewed up-close, owl feathers appear velvety. The furry texture absorbs and dampens sound like a sound blanket. It also allows the feathers to quietly slide past each other in flight, reducing rusting sounds.
--- Why do owls hunt at night?
Owls belong to a group called raptors which also so includes with hawks, eagles and falcons. Most of these birds of prey hunt during the day and rely on. But unlike most other raptors, the roughly 200 species of owl are generally nocturnal while others are crepuscular, meaning that they’re active around dawn and dusk.
They have extremely powerful low-light vision, and finely tuned hearing which allows them to locate the source of even the smallest sound. Owls simply hide and wait for their prey to betray its own location. As ambush hunters, owls tend to rely on surprise more often than their ability to give chase.
--- Why do owls hoot?
With Halloween around the corner, you might have noticed a familiar sound in the night. It’s mating season for owls and the sound of their hooting fills the darkness.
According to Chris Clark, an an assistant professor of biology at UC Riverside,, “The reason why owls are getting ready to breed right now in the late fall is because they breed earlier than most birds. The bigger the bird the longer it takes for them to incubate their eggs and for the nestlings to hatch out and or the fledglings to leave the nest. Owls try to breed really early because they want their babies to be leaving the nest and practicing hunting right when there are lots of baby animals around like baby rabbits that are easy prey.”
--- More great DEEP LOOK episodes:
Halloween Special: Watch Flesh-Eating Beetles Strip Bodies to the Bone
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Np0hJGKrIWg
What Happens When You Put a Hummingbird in a Wind Tunnel?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JyqY64ovjfY
You're Not Hallucinating. That's Just Squid Skin.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0wtLrlIKvJE
--- Super videos from the PBS Digital Studios Network!
Did Dinosaurs Really Go Extinct? - It's Okay to be Smart
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3_RLz0whDv4
The Surprising Ways Death Shapes Our Lives - BrainCraft
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Joalg73L_gw
Crazy pool vortex - Physics Girl
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pnbJEg9r1o8
--- More KQED SCIENCE:
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
KQED Science: http://www.kqed.org/science
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios and the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is supported by HopeLab, The David B. Gold Foundation; S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation; The Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation; The Vadasz Family Foundation; Smart Family Foundation and the members of KQED.
#deeplook
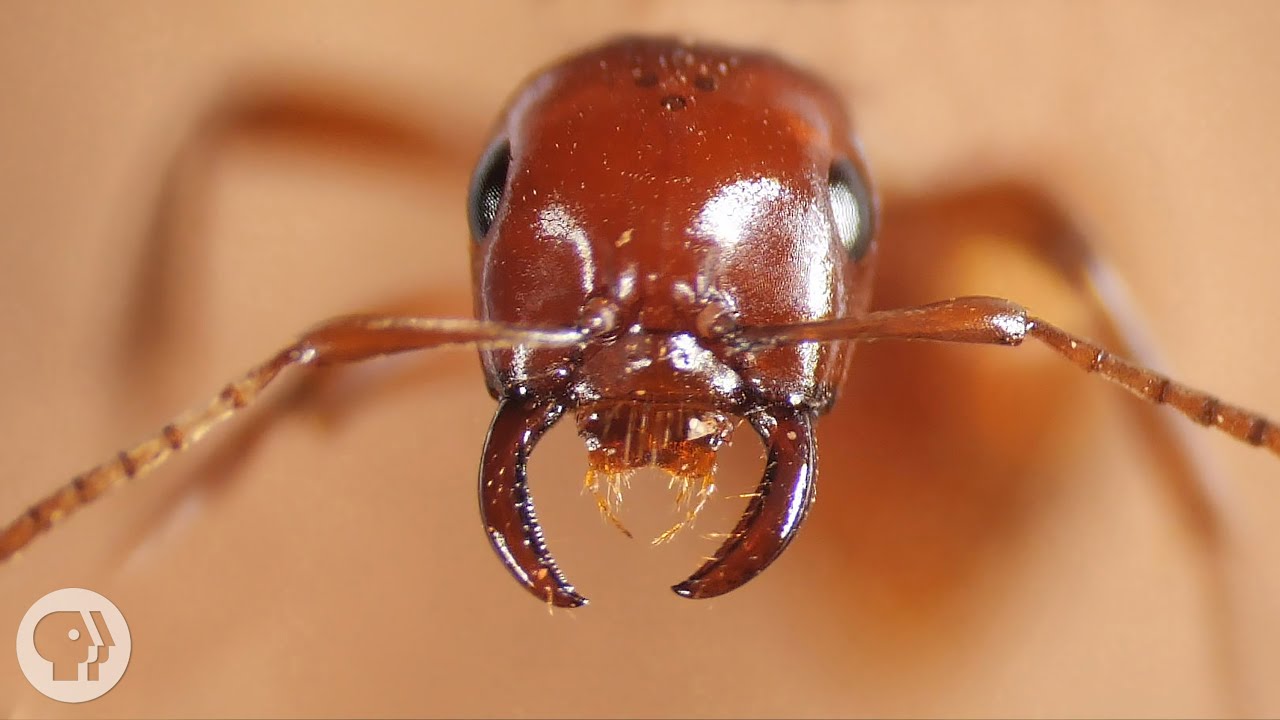
Kidnapper ants raid other ant species' colonies, abduct their young and take them back to their nest. When the enslaved babies grow up, the kidnappers trick them into serving their captors – hunting, cleaning the nest, even chewing up their food for them.
Please join our community on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK is a ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
A miniature drama is playing out on the forest floor in California’s preeminent mountain range, the Sierra Nevada, at this time of year. As the sun sets, look closely and you might see a stream of red ants frantically climbing over leaves and rocks.
They aren’t looking for food. They’re looking for other ants. They’re kidnappers.
“It’s hard to know who you're rooting for in this situation,” says Kelsey Scheckel, a graduate student at UC Berkeley who studies kidnapper ants. “You're just excited to be a bystander.”
On this late summer afternoon, Scheckel stares intently over the landscape at the Sagehen Creek Field Station, part of the University of California’s Natural Reserve System, near Truckee, California.“The first thing we do is try to find a colony with two very different-looking species cohabitating,” Scheckel says.
“That type of coexistence is pretty rare. As soon as we find that, we can get excited.”
--- How do ants communicate?
Ants mostly use their sense of smell to learn about the world around themselves and to recognize nestmates from intruders. They don’t have noses. Instead, they use their antennae to sense chemicals on surfaces and in the air. Ants’ antennae are porous like a kitchen sponge allowing chemicals to enter and activate receptors inside. You will often see ants tap each other with their antennae. That behavior, called antennation, helps them recognize nestmates who will share the same chemical nest signature.
---Can ants bite or sting?
Many ants will use their mandibles, or jaws, to defend themselves but that typically just feels like a pinch. Some ants have a stinger at the end of their abdomen that can deliver a venomous sting. While the type of venom can vary across species, many ants’ sting contains formic acid which causes a burning sensation. Some have special glands containing acid that can spray at attackers causing burning and alarming odors.
---+ Read the entire article on KQED Science:
https://www.kqed.org/science/1....947369/kidnapper-ant
---+ For more information:
Neil Tsutsui Lab of Evolution, Ecology and Behavior of Social Insects at the University of California, Berkeley
https://nature.berkeley.edu/tsutsuilab/
---+ Shoutout!
?Congratulations ?to the following fans for correctly naming and describing the inter-species, mandible-to-mandible ant behavior we showed on our Deep Look Community Tab… "trophallaxis:"
Senpai
Ravinraven6913
CJ Thibeau
Maksimilian Tašler
Isha
https://www.youtube.com/channe....l/UC-3SbfTPJsL8fJAPK
---+ Thank you to our Top Patreon Supporters ($10+ per month)!
Leonhardt Wille
Justin Bull
Bill Cass
Sarah Khalida Mohamad
Daniel Weinstein
Chris B Emrick
Karen Reynolds
Tea Torvinen
David Deshpande
Daisuke Goto
Companion Cube
WhatzGames
Richard Shalumov
Elizabeth Ann Ditz
Gerardo Alfaro
Robert Amling
Shirley Washburn
Robert Warner
Supernovabetty
johanna reis
Kendall Rasmussen
Pamela Parker
Sayantan Dasgupta
Joshua Murallon Robertson
Cindy McGill
Kenia Villegas
Shelley Pearson Cranshaw
Aurora
Dean Skoglund
Silvan Wendland
Ivan Alexander
monoirre
Sonia Tanlimco
Two Box Fish
Jane Orbuch
Allen
Laurel Przybylski
Johnnyonnyful
Rick Wong
Levi Cai
Titania Juang
Nathan Wright
Carl
Michael Mieczkowski
Kyle Fisher
JanetFromAnotherPlanet
Kallie Moore
SueEllen McCann
Geidi Rodriguez
Louis O'Neill
Edwin Rivas
Jeanne Sommer
Katherine Schick
Aurora Mitchell
Cory
Ricardo Martinez
riceeater
Daisy Trevino
KW
PM Daeley
Joao Ascensao
Chris Murphy
Nicolette Ray
TierZoo
---+ Follow KQED Science and Deep Look:
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/kqedscience/
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
KQED Science on kqed.org: http://www.kqed.org/science
Facebook Watch: https://www.facebook.com/DeepLookPBS/
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate in San Francisco, CA, serves Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial TV, Radio and web media.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is also supported by the National Science Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Fuhs Family Foundation, Campaign 21 and the members of KQED.
Take the PBSDS survey: https://to.pbs.org/2018YTSurvey
Explore our VR slug and support us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
Nudibranchs may look cute, squishy and defenseless ... but watch out. These brightly-colored sea slugs aren't above stealing weapons from their prey.
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK is a ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
The summer months bring low morning tides along the California coast, providing an opportunity to see one of the state’s most unusual inhabitants, sea slugs.
Also called nudibranchs, many of these relatives of snails are brightly colored and stand out among the seaweed and anemones living next to them in tidepools.
“Some of them are bright red, blue, yellow -- you name it,” said Terry Gosliner, senior curator of invertebrate zoology and geology at the California Academy of Sciences in San Francisco. “They're kind of designer slugs.”
But without a protective shell, big jaws or sharp claws, how do these squishy little creatures get away with such flamboyant colors in a habitat full of predators?
As it turns out, the nudibranchs’ colors serve as a warning to predators: These sea slugs are packing some very sophisticated defenses. And some aren’t above stealing weapons from their prey.
Gosliner and Brenna Green and Emily Otstott, graduate students at San Francisco State University, were out at dawn earlier this summer searching tidepools and floating docks around the Bay Area. They want to learn more about how these delicate little sea slugs survive and how changing ocean temperatures might threaten their futures.
Nudibranchs come in a staggering variety of shapes and sizes. Many accumulate toxic or bad-tasting chemicals from their prey, causing predators like fish and crabs to learn that the flashy colors mean the nudibranch wouldn’t make a good meal.
--- What are nudibranchs?
Nudibranchs are snails that lost their shell over evolutionary time. Since they don’t have a shell for protection, they have to use other ways to defend themselves like accumulating toxic chemicals in their flesh to make them taste bad to predators. Some species of nudibranchs eat relatives of jellyfish and accumulate the stingers within their bodies for defense.
--- Why do nudibranchs have such bright colors?
The bright colors serve as a signal to the nudibranch’s predators that they are not good to eat. If a fish or crab bites a nudibranch, it learns to associate the bad taste with the bright colors which tends to make them reluctant to bite a nudibranch with those colors in the future.
--- What does nudibranch mean?
The word nudibranch comes from Latin. It means naked gills. They got that name because some species of nudibranchs have an exposed ring of gills on their back that they use to breath.
---+ Read the entire article on KQED Science:
https://www.kqed.org/science/1....929993/this-adorable
---+ For more information:
Learn more about Terry Gosliner’s work with nudibranchs
https://www.calacademy.org/sta....ff/ibss/invertebrate
Learn more about Chris Lowe’s work with plankton
http://lowe.stanford.edu/
Learn more about Jessica Goodheart’s study of nematocyst sequestration
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.co....m/doi/full/10.1111/i
---+ More Great Deep Look episodes:
From Drifter to Dynamo: The Story of Plankton | Deep Look
https://youtu.be/jUvJ5ANH86I
For Pacific Mole Crabs It's Dig or Die | Deep Look
https://youtu.be/tfoYD8pAsMw
The Amazing Life of Sand | Deep Look
https://youtu.be/VkrQ9QuKprE
---+ See some great videos and documentaries from PBS Digital Studios!
Why Are Hurricanes Getting Stronger? | Hot Mess
https://youtu.be/2E1Nt7JQRzc
When Fish Wore Armor | Eons
https://youtu.be/5pVTZH1LyTw
Why Do We Wash Our Hands After Going to the Bathroom? | Origin of Everything
https://youtu.be/fKlpGs34-_g
---+ Follow KQED Science and Deep Look:
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/kqedscience/
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
KQED Science on kqed.org: http://www.kqed.org/science
Facebook Watch: https://www.facebook.com/DeepLookPBS/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/deeplook
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate in San Francisco, CA, serves Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial TV, Radio and web media.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is supported by the Templeton Religion Trust and the Templeton World Charity Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Fuhs Family Foundation Fund and the members of KQED.
#deeplook #nudibranch #seaslug
Dermestid Beetles are fast and fastidious eaters. They can pick a carcass clean in just days leaving even the most delicate bone structures intact. This makes them the perfect tool for museum scientists-- if you keep them far, far away from valuable collections.
SUBSCRIBE: http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
In nature, Dermestid Beetles are death-homing devices. They’ll find a dead body about a week after death and lay eggs in the drying flesh. The larvae emerge with a voracious appetite, outgrowing their skins six to eight times in just days before pupating, becoming adults and flying away to start a new colony.
These Dermestid Beetles at the Museum of Vertebrate Zoology at UC Berkeley are direct descendants from the original colony established in this museum in 1924. The process now used at museums around the world was pioneered here. These are the beetles you see here in this flesh-eating beetles time lapse.
Scientists in the prep lab downstairs receive nearly a thousand carcasses a year. It’s their job to preserve each animal for long-term use in the collections upstairs. And the work is not for the squeamish.
What makes beetles ideal for cleaning museum specimens is that they’re fast and fastidious eaters. They can pick a carcass clean while leaving even the most delicate bone structures intact.
It takes a large beetle colony 24 – 48 hours to clean the bones of small animals like rabbits and owls, and they can work on 100 - 200 specimens at a time. Larger animals like deer or coyotes take about a week.
But the alliance between beetles and museum is an uneasy one. Downstairs the beetles are a critical tool. But if Dermestids got loose upstairs, they could wreak havoc in the library stacks, munching through specimen drawers and ruining entire collections.
--- More KQED SCIENCE:
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
KQED Science: http://ww2.kqed.org/science
---
More great DEEP LOOK episodes:
Where Are the Ants Carrying All Those Leaves?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-6oKJ5FGk24
What Happens When You Put a Hummingbird in a Wind Tunnel?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JyqY64ovjfY
Pygmy Seahorses: Masters of Camouflage
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q3CtGoqz3ww
Related videos from the PBS Digital Studios Network!
Can Microbes Solve Murder Mysteries? - Gross Science
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kRUt9pqMCSg
The Surprising Ways Death Shapes Our Lives - BrainCraft
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Joalg73L_gw
Do Animals Mourn Their Dead? - It's Okay to Be Smart (ft. BrainCraft and Gross Science!)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rHJDmMSKlHM
--- More KQED SCIENCE:
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
KQED Science: http://ww2.kqed.org/science
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios and the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is supported by HopeLab, The David B. Gold Foundation; S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation; The Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation; The Vadasz Family Foundation; Smart Family Foundation and the members of KQED.
#deeplook #dermestids #dermestidbeetle
The Peruvian Amazon is a dangerous place when you're small. So the young Inga tree hires ants as bodyguards to protect its vulnerable leaves. Their pay: delicious nectar served up in tiny ant-sized dishes. But will the ants keep up their end of the bargain?
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK is a ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Get a new perspective on our place in the universe. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
* NEW VIDEOS EVERY OTHER TUESDAY! *
For some, ants are welcome guests. In the Amazon rainforest of Peru, a type of tree called the Inga actively encourages ants to stick around.
The tree, which is related to plants that produce beans and other legumes, grows tiny structures near the base of its leaves, called nectaries, that secrete a sugary fluid to feed to the ants. In turn, the ants serve as bodyguards, protecting the Inga and its nectaries from invading herbivores.
“Plants have all kinds of defenses, but because Inga leaves are not as toxic as many other plants,” says Suzanne Koptur, a professor of biology at Florida International University, “they’re good food for herbivores of all sizes and shapes, from big mammals like sloths and monkeys to little invertebrates like caterpillars.“
The rainforest is especially dangerous for young trees. The branches and leaves of mature trees merge together high in the air forming a canopy. Young trees on the forest floor struggle to get enough light. Young trees also have fewer leaves, and losing even a few to herbivores can threaten their survival.
They may be small, but few species want to tangle with the aggressive and territorial big-headed ants.
"Ants have powers in numbers, especially if they bite and sting," says Koptur.
The ants keep most herbivores, especially hungry caterpillars, away from the young trees. Simply put, the trees provide nectar to the ants in exchange for protection.
--- What is mutualism?
In biology, mutualism refers to a relationship between two organisms that benefits both of parties. Mutualism is one type of symbiotic relationship.
--- What are caterpillars?
Caterpillars are the larvae of butterflies and caterpillars. Young caterpillars hatch out of eggs, eat, grow and molt. They eventually pupate inside their cocoons and then emerge as winged adults.
--- What is plant nectar?
Nectar is a sugary liquid secreted by plants through structures called nectaries. Nectaries are commonly found in flowers to attract pollinators. Some plants also have extra-floral nectaries located outside of the flowers. To attract animals including ants and predatory wasps that protect the plant from herbivores.
---+ Read the entire article on KQED Science:
https://ww2.kqed.org/science/2....016/11/01/the-double
---+ For more information:
Interactions Among Inga, Herbivores, Ants, and Insect Visitors to Foliar Nectaries
http://faculty.fiu.edu/~koptur....s/pubs/MVbookIngaAnt
---+ More Great Deep Look episodes:
Winter is Coming For These Argentine Ant Invaders
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=boyzWeHdtiI
Where Are the Ants Carrying All Those Leaves?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-6oKJ5FGk24
This Vibrating Bumblebee Unlocks a Flower's Hidden Treasure
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-6oKJ5FGk24
---+ See some great videos and documentaries from the PBS Digital Studios!
It's Okay to Be Smart: Why Don't Ants Get Stuck In Traffic?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kkiuw0HbRq4
Gross Science: The World's Most Expensive Fungus
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iV4WHFU2Id8
---+ Follow KQED Science:
KQED Science: http://www.kqed.org/science
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate based in San Francisco, serves the people of Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial media. Home to one of the most listened-to public radio station in the nation, one of the highest-rated public television services and an award-winning education program, KQED is also a leader and innovator in interactive media and technology, taking people of all ages on journeys of exploration — exposing them to new people, places and ideas.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios and the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is also supported by HopeLab, the David B. Gold Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Smart Family Foundation and the members of KQED. macro documentary
#deeplook
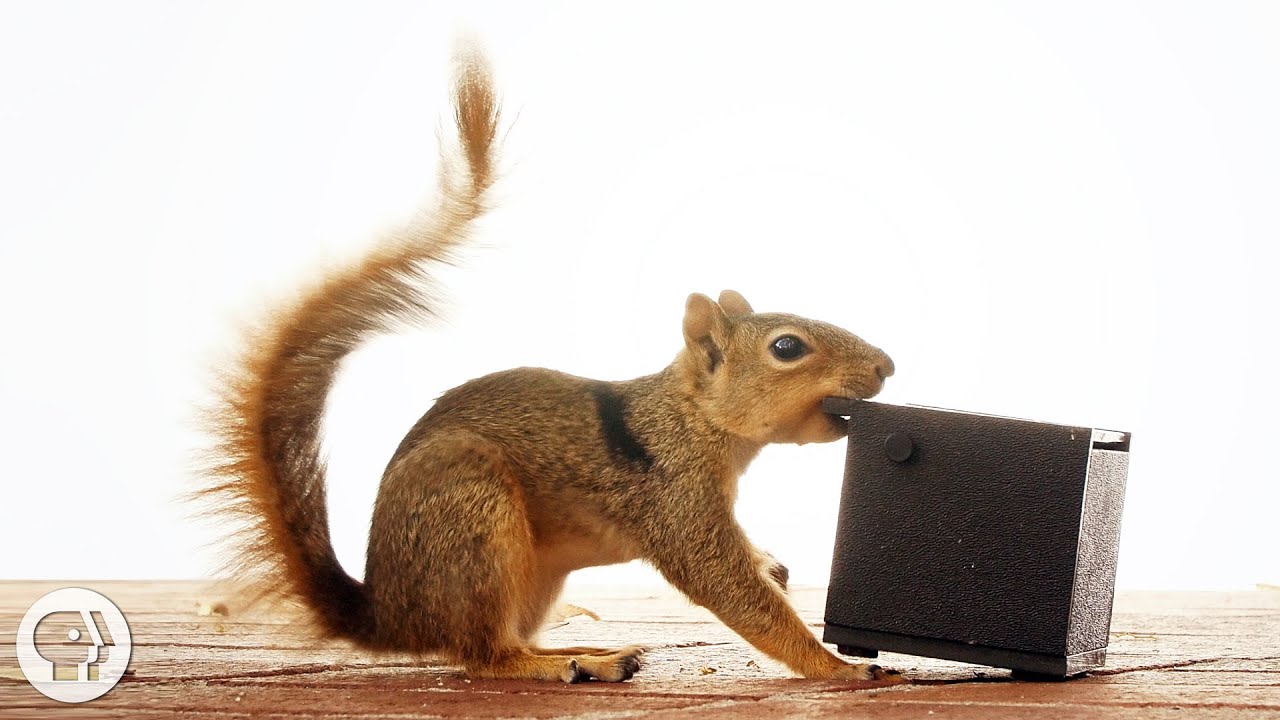
Humans aren’t the only creatures that get frustrated. Squirrels do too. One researcher wants to know, could there be an evolutionary benefit to losing your cool?
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK is a ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Get a new perspective on our place in the universe and meet extraordinary new friends. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
* NEW VIDEOS EVERY OTHER TUESDAY! *
YouTube viewers are well-acquainted with the squirrel genre: Thousands of videos that show squirrels going to great lengths to extract seeds from bird feeders (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FgDa_cpgHWs), or the old favorite, squirrels stuffing their cheeks (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_15UrPHkVQo).
Maybe squirrels are so popular because we see some of ourselves in them. This is part of what fueled Mikel Delgado’s interest in the fox squirrels she saw at the University of California, Berkeley. An animal behaviorist and doctoral student there, she likes to quote from Charles Darwin’s book “The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex,” in which the English naturalist proposed that the differences between humans and other animals aren’t that clear-cut.
“It was controversial because people thought animals were machines and didn’t feel pain,” she said.
Inspired by Darwin, Delgado was intrigued by squirrels’ emotional worlds. The way to tell what they’re feeling, researchers have found, is to watch their tails. When threatened by a predator like a dog, a fox squirrel whips its tail in an s-shaped pattern that researchers call “flagging.”
Delgado wondered what else she could learn from watching squirrels flag their tails. For instance, do they get frustrated, the way that people do? So she devised an experiment to explore this question.
She taught some of the fox squirrels on campus to lift the lid of a plastic box to find a walnut inside. When the squirrel ate the nut, she dropped another one in. This way, she trained the squirrels to expect a walnut when they looked inside. This training was important because frustration is usually defined as not getting what you expect.
Then she replaced the walnut with corn – which squirrels don’t like as much – or left the box empty. These squirrels flagged their tails. For a third group, she locked the box. They flagged their tails the most. They got aggressive, a hallmark of frustration. And they bit, toppled and dragged the box, trying to open it.
That makes Delgado think that perhaps frustration has an evolutionary purpose, that it isn’t just for blowing off steam, but is instead a way to gather up energy to “brute-force” a solution.
--+ Is frustration an emotion?
“It’s a little bit controversial,” said Delgado. “It depends on who you talk to.”
Researchers don’t consider frustration one of the basic, or universal, emotions. In the 1960s, psychologist Paul Ekman identified six universal emotions: joy, anger, sadness, surprise, fear and disgust:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-PFqzYoKkCc
Frustration is related to anger, but researchers don’t consider frustration a basic emotion. “There’s a question as to what exactly it is,” said Delgado. “Sometimes you see it described very specifically as a task: For example, when you expect a soda and you don’t get it from the vending machine. And sometimes you see it described as the response to the task.”
---+ Read the entire article on KQED Science:
https://ww2.kqed.org/science/2....016/09/20/watch-thes
---+ For more information:
The lab of Lucia Jacobs, where Mikel Delgado does her research: http://jacobs.berkeley.edu/
---+ More Great Deep Look episodes:
Can a New “Vaccine” Stem the Frog Apocalypse?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-IXVcyCZVBg
These Crazy Cute Turtles Want Their Lake Back
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YTYFdpNpkMY
---+ See some great videos and documentaries from PBS Digital Studios!
BrainCraft: The Power of Sadness in Inside Out
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ST97BGCi3-w
PBS Idea Channel: 3 Fallacies For Election Season!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=REp4zCum3XY
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate in San Francisco, CA, serves Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial TV, Radio and web media.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios and the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is also supported by HopeLab, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Smart Family Foundation and the members of KQED.
#deeplook #squirrel #squirrelbehavior
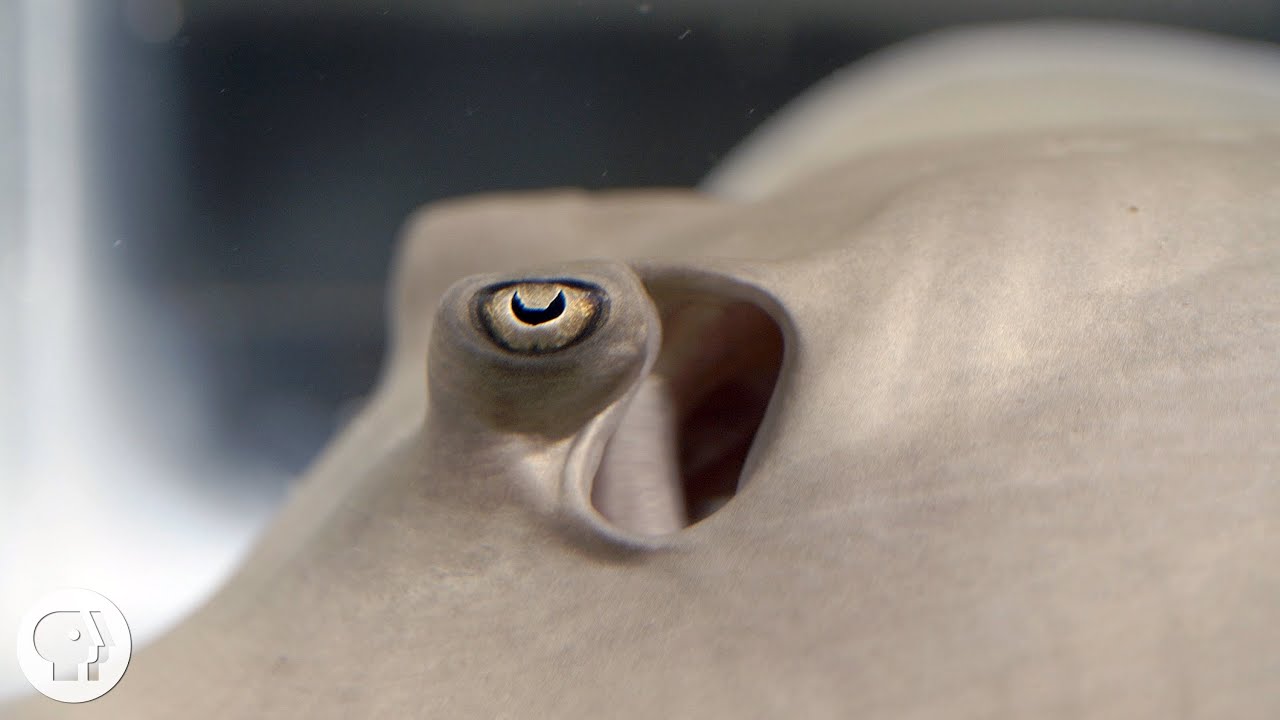
When it comes to spotting prey, sharks and rays have a secret sense beyond sight and smell. Tiny goo-filled organs called Ampullae of Lorenzini detect the invisible electric fields produced by all living creatures.
DEEP LOOK: a new ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Get a new perspective on our place in the universe and meet extraordinary new friends. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
How do Sharks and Rays Sense Electric Fields?
Most animals don’t have the ability to detect electric fields. But sharks, rays, skates and sawfish — members of a group called Elasmobranchii — are masters of detecting electric signals. It’s one of their defining features. Elasmobranchs have specialized organs called Ampullae of Lorenzini. These tiny structures allow them to home in on weak bioelectric fields generated by nearby prey.
Elasmobranch’s electrosensory organs are named after a 17th century Italian physician, Stefano Lorenzini, who first identified them while dissecting an electric ray. Lorenzini noticed dozens of tiny pores around the animal’s mouth. Each of the pores led to jelly-filled canals that ended in pocket-like structures that he called ampullae, the Latin word for a type of round-bottomed flask.
Animals emit low frequency electric fields due to a process known as osmoregulation. This process allows the concentration of ions (charged atoms or molecules) to flow between the inside of our bodies and the outside. In order for our cells to stay intact, the flow of ions needs to be balanced.
But balanced doesn’t necessarily mean equal. The concentration of ions within a shrimp’s body is much lower than that of the sea water it swims in. Their voltage, or potential difference generated between the two concentrations across “leaky” surfaces, can then be detected by the ampullae.
More KQED SCIENCE:
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
KQED Science: http://ww2.kqed.org/science
---
Read the article for this video on KQED Science:
http://ww2.kqed.org/science/2015/08/11/sharks-and-rays-sense-electricity-fish-cant-hide/
#deeplook
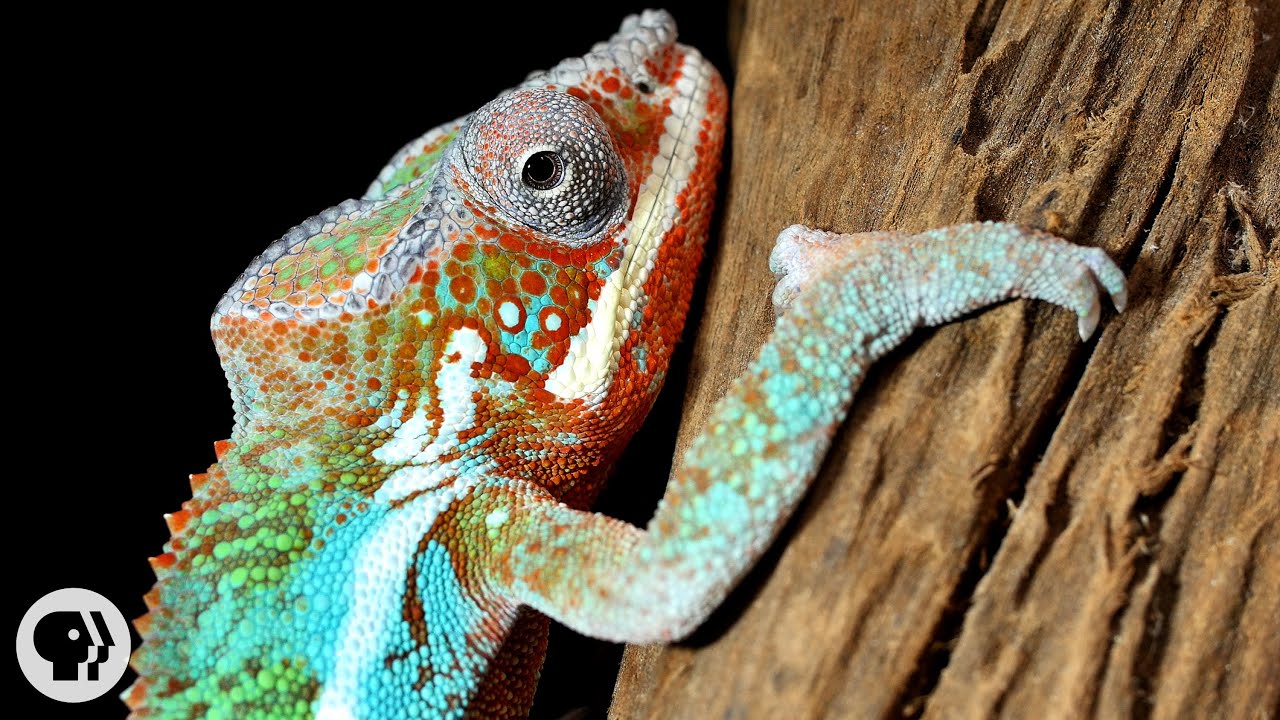
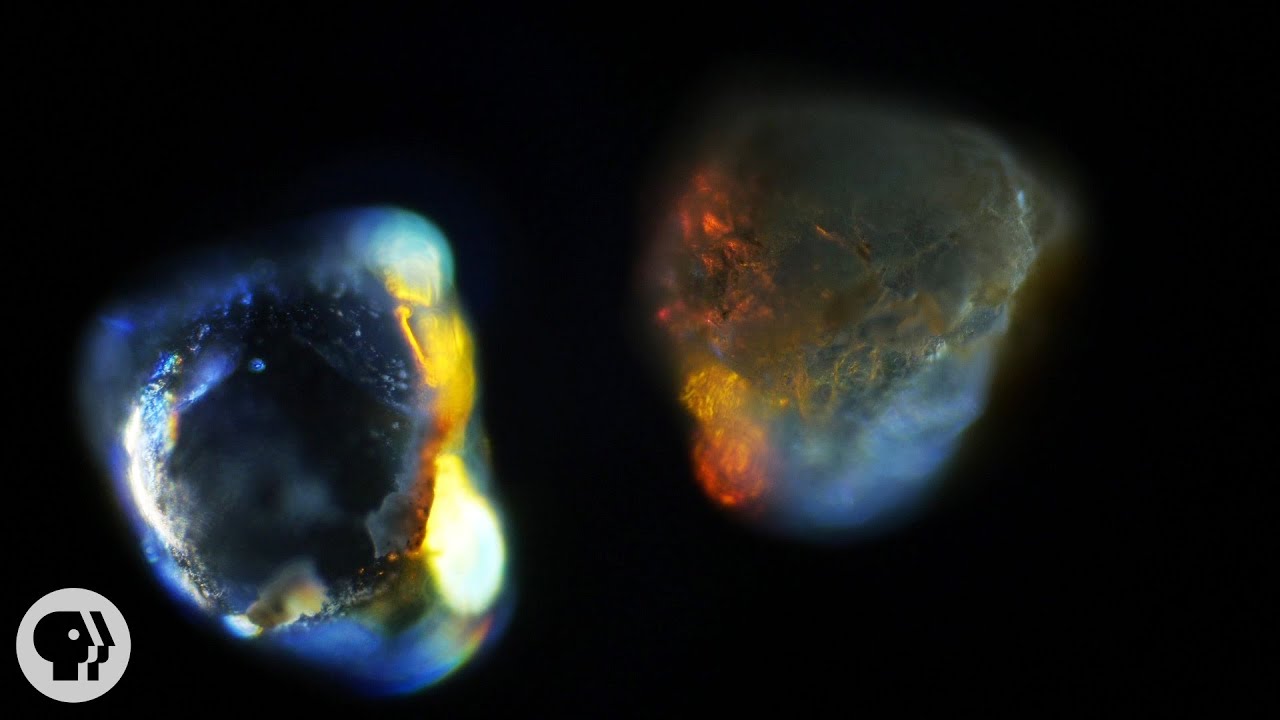
Chameleons don't change color to match their environment; it’s just the opposite. How do they do it? By manipulating tiny crystals in their skin. Now, UC Berkeley researchers are on a quest to create synthetic chameleon skin inspired by these reptiles’ uncanny ability.
DEEP LOOK: a new ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Get a new perspective on our place in the universe and meet extraordinary new friends. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
--- How do Chameleons Change Color?
Chameleons are some of the most brilliantly colored animals on the planet. But how did they evolve the ability to change color?
Scientists used to believe that chameleons changed color by spreading out pigments in their skin, much like octopuses or squid do.
The top layer of chameleon skin – called the epidermis – contains yellow pigment cells called xanthophores, and red pigment cells called erythrophores. But the amount of pigment in the cells stays the same, even when the chameleon changes color.
Just beneath the chameleon’s skin is a layer of cells called iridophores. These cells contain microscopic salt crystals, which are arranged in a three-dimensional pattern like oranges stacked on a fruit stand.
When light hits the crystals, some wavelengths are absorbed and some are reflected. The result, to our eyes, is the beautiful rainbow of colors on the chameleon’s skin. But what we’re actually seeing is light that is bouncing off of these tiny crystals. What we perceive as green, for example, is blue wavelengths of light being reflected off the crystals and through the layer of yellow xanthophore cells in the chameleon’s epidermis. The result is bright green skin that contains no green pigment!
The process of changing color is called metachrosis.
--- Why do Chameleons Change Color?
Chameleons don’t change color to match their environment. In fact, it’s just the opposite.
Their baseline is camouflage.
When chameleons are relaxed, they’re mostly green. They naturally blend into their home in the forest canopy. They even mimic leaves by dancing around a little.
But when they feel threatened, annoyed, or just want to show a little swagger, that’s when their color changes.
Scientists once thought that chameleons color-changing abilities allowed them to better camouflage themselves. Most species of chameleons live high in the forest canopy and their various shades of green provide natural camouflage. Even their movement provides camouflage – they dance around to mimic leaves blowing in the wind.
In fact, chameleons change color primarily to communicate with each other, as though they were living mood rings. Males will warn each other about their territory and females will change color to let males know whether they’re interested in breeding.
Chameleons also have a second layer of iridiophore cells just beneath the first. The crystals in that layer are larger and reflect light waves in the infrared wavelengths. This suggests that chameleons are also changing colors to regulate their temperature, according to Milinkovitch. Chameleons are cold-blooded and heat their bodies with the warmth of the sun.
Read the article for this video on KQED Science:
http://ww2.kqed.org/science/20....15/08/25/natures-moo
--- More great DEEP LOOK episodes:
Where Are the Ants Carrying All Those Leaves?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-6oKJ5FGk24
What Happens When You Put a Hummingbird in a Wind Tunnel?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JyqY64ovjfY
Pygmy Seahorses: Masters of Camouflage
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q3CtGoqz3ww
--- Related video from the PBS Digital Studios Network!
Nature's Most Amazing Animal Superpowers - It’s Okay to be Smart
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e69yaWDkVGs
--- Other Great Science Videos About Chameleons
How Do Chameleons Change Color? - Veritasium
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SQggDnScsvI
True Facts About The Chameleon - zefrank1
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UR_byRbXxvs
--- More KQED SCIENCE:
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
KQED Science: http://ww2.kqed.org/science
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios and the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is supported by HopeLab, The David B. Gold Foundation; S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation; The Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation; The Vadasz Family Foundation; Smart Family Foundation and the members of KQED.
#deeplook
Are You Smarter Than A Slime Mold? Let’s go ask Joe Hanson: https://youtu.be/K8HEDqoTPgk
SUBSCRIBE to Deep Look! http://goo.gl/8NwXqt
DEEP LOOK: a new ultra-HD (4K) short video series created by KQED San Francisco and presented by PBS Digital Studios. See the unseen at the very edge of our visible world. Get a new perspective on our place in the universe and meet extraordinary new friends. Explore big scientific mysteries by going incredibly small.
---+ About Slime Molds
Flip over a rotting log and chances are you’ll see a goopy streak stuck to the wood. If you were to film this goop and play the video back in high speed, you’d see something that might remind you of the 1950s sci-fi classic “The Blob:” a jelly-like creature pulsating in a strange way, a little bit forward, a little bit back, spreading and searching for something to devour.
But this creature isn’t intent on world domination. It’s a slime mold, a very simple organism that is neither plant, nor animal, nor fungus. Unlike the cells of other living beings, which have only one nucleus that carries their genetic information, slime molds can organize into something like a cell with thousands of nuclei. Slime molds may move slowly, but they excite scientists by their ability to get a lot done with very little.
Researchers at the University of California San Diego and UC Davis have been focusing their attention on how slime molds get around, in the hope of inspiring a new generation of soft-bodied robots with medical applications.
Slime molds don’t have legs or any appendages. They eat bacteria and tiny fungi. And they move just by changing their shape.
“It’s intriguing to understand how they can move when they’re softer than the environment,” said UC San Diego engineer Juan Carlos Del Alamo. “The absence of limbs makes it a difficult problem.”
Slime mold’s locomotion is triggered by a chemical reaction. In the lab, Del Alamo and his colleagues cut off small pieces of a bright yellow slime mold called Physarum polycephalum and put them under a microscope. They watched each piece squeeze itself. This contraction is triggered by tiny calcium ions flowing inside it. The slime mold contracts its wall, then sloshes to move the calcium ions back so that they can trigger another contraction – at least that’s the researchers’ hypothesis.
---+ What are slime molds?
Let’s start with what they’re not. They can stand upright and produce spores. But they’re not fungi or plants. When they’re hungry, they spread across the forest chasing food such as tiny fungi or bacteria. But they’re not animals.
---+ Where are slime molds often found?
Slime molds are often found under rotting logs. You can also order the bright yellow slime mold in our video, Physarum polycephalum, from biological supplies companies. They’re fun to grow at home.
---+ What do slime molds eat?
In nature, slime molds eat tiny fungi and bacteria. When they’re grown in the lab, researchers feed them oats.
Read the entire article on KQED Science:
https://ww2.kqed.org/science/2....016/04/19/this-pulsa
---+ More great DEEP LOOK episodes:
Can A Thousand Tiny Swarming Robots Outsmart Nature?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dDsmbwOrHJs
This Mushroom Starts Killing You Before You Even Realize It
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bl9aCH2QaQY
Banana Slugs: Secret of the Slime
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mHvCQSGanJg&nohtml5=False
---+ More videos and documentaries from the PBS Digital Studios!
Gross Science: Why Am I Obsessed With Gross Stuff?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8dfVN5w3_Y4
BrainCraft: The Prisoner's Dilemma
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p1KU7i5hpM8
---+ Follow KQED Science:
KQED Science: http://www.kqed.org/science
Tumblr: http://kqedscience.tumblr.com
Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/kqedscience
---+ About KQED
KQED, an NPR and PBS affiliate based in San Francisco, serves the people of Northern California and beyond with a public-supported alternative to commercial media. KQED is also a leader and innovator in interactive media and technology, taking people of all ages on journeys of exploration — exposing them to new people, places and ideas.
Funding for Deep Look is provided in part by PBS Digital Studios and the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation. Deep Look is a project of KQED Science, which is also supported by HopeLab, the David B. Gold Foundation, the S. D. Bechtel, Jr. Foundation, the Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation, the Vadasz Family Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Smart Family Foundation and the members of KQED.
#deeplook
![Ultravox - Sleepwalk - TOTP 1980 [HD]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TtJ2qU-HTLs/maxresdefault.jpg)